Page 217 - Concise Encyclopedia of Robotics
P. 217
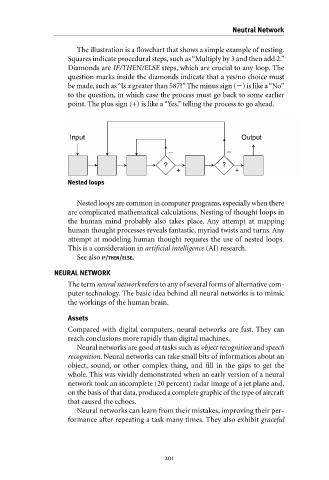
The illustration is a flowchart that shows a simple example of nesting.
Squares indicate procedural steps, such as “Multiply by 3 and then add 2.”
Diamonds are IF/THEN/ELSE steps, which are crucial to any loop. The
question marks inside the diamonds indicate that a yes/no choice must
be made, such as “Is x greater than 587?”The minus sign ( ) is like a “No”
to the question, in which case the process must go back to some earlier
point. The plus sign (+) is like a “Yes,” telling the process to go ahead.
Output
Input Neutral Network
_ _
? ?
+ +
Nested loops
Nested loops are common in computer programs,especially when there
are complicated mathematical calculations. Nesting of thought loops in
the human mind probably also takes place. Any attempt at mapping
human thought processes reveals fantastic, myriad twists and turns. Any
attempt at modeling human thought requires the use of nested loops.
This is a consideration in artificial intelligence (AI) research.
See also IF/THEN/ELSE.
NEURAL NETWORK
The term neural network refers to any of several forms of alternative com-
puter technology. The basic idea behind all neural networks is to mimic
the workings of the human brain.
Assets
Compared with digital computers, neural networks are fast. They can
reach conclusions more rapidly than digital machines.
Neural networks are good at tasks such as object recognition and speech
recognition. Neural networks can take small bits of information about an
object, sound, or other complex thing, and fill in the gaps to get the
whole. This was vividly demonstrated when an early version of a neural
network took an incomplete (20 percent) radar image of a jet plane and,
on the basis of that data,produced a complete graphic of the type of aircraft
that caused the echoes.
Neural networks can learn from their mistakes, improving their per-
formance after repeating a task many times. They also exhibit graceful