Page 213 - Concise Encyclopedia of Robotics
P. 213
Motor
MODULUS
See NUMERATION.
MOS
See METAL-OXIDE SEMICONDUCTOR (MOS).
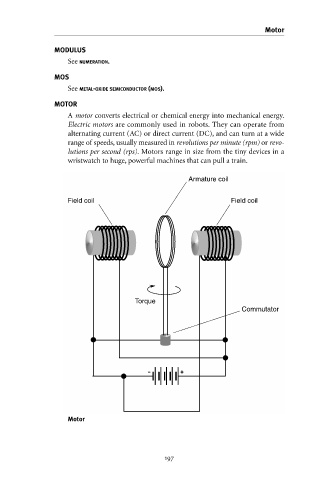
MOTOR
A motor converts electrical or chemical energy into mechanical energy.
Electric motors are commonly used in robots. They can operate from
alternating current (AC) or direct current (DC), and can turn at a wide
range of speeds, usually measured in revolutions per minute (rpm) or revo-
lutions per second (rps). Motors range in size from the tiny devices in a
wristwatch to huge, powerful machines that can pull a train.
Armature coil
Field coil Field coil
Torque
Commutator
Motor