Page 229 - Concise Encyclopedia of Robotics
P. 229
An occupancy grid can be rendered in three dimensions (3-D) by
assigning the probabilities to values on an axis perpendicular to the plane
of the grid itself.The regions of highest probability thus appear as “hills”or
“mountains” while the regions of lowest probability appear as “valleys”
or “canyons.”
See also COMPUTER MAP, QUADTREE, RADAR, and SONAR.
OCTAL NUMBER SYSTEM
See NUMERATION. Odometry
OCTREE
See QUADTREE.
ODOMETRY
Odometry is a means of position sensing. It allows a robot to figure out
where it is on the basis of two things: (1) a starting point, and (2) the
motions it has made after having departed from that point.
Along a straight line, or in one dimension, odometry is performed by
the mileage indicator in a car. The displacement, or distance traveled, is
determined by counting the number of wheel rotations, based on a certain
wheel radius. (If you switch to larger or smaller tires, you must realign
the odometer in the car to get accurate readings.)
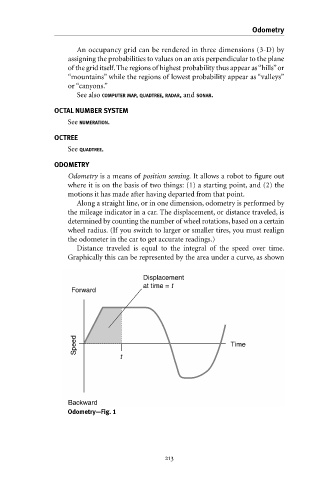
Distance traveled is equal to the integral of the speed over time.
Graphically this can be represented by the area under a curve, as shown
Displacement
at time = t
Forward
Speed Time
t
Backward
Odometry—Fig. 1