Page 95 - Concise Encyclopedia of Robotics
P. 95
Domain of Function
DOMAIN OF FUNCTION
The domain of a mathematical function is the set of independent-variable
values for which the function is defined. Every x in the domain of a func-
tion f is mapped by f onto a definite, single value y. Any x not in the do-
main is not mapped onto anything by the function f.
1/2
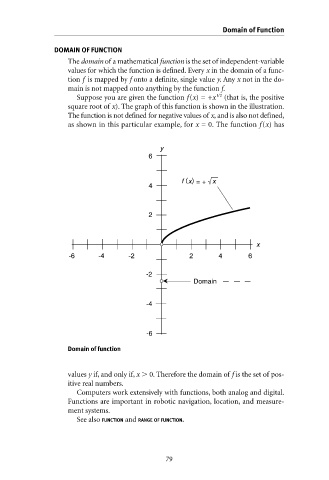
(that is, the positive
Suppose you are given the function f(x) = +x
square root of x). The graph of this function is shown in the illustration.
The function is not defined for negative values of x, and is also not defined,
as shown in this particular example, for x = 0. The function f (x) has
y
6
f ( ) x
x = +
4
2
x
-6 -4 -2 2 4 6
-2
Domain
-4
-6
Domain of function
values y if, and only if, x 0. Therefore the domain of f is the set of pos-
itive real numbers.
Computers work extensively with functions, both analog and digital.
Functions are important in robotic navigation, location, and measure-
ment systems.
See also FUNCTION and RANGE OF FUNCTION.