Page 155 - Control Theory in Biomedical Engineering
P. 155
Modeling simple and complex handwriting based on EMG signals 139
0.08 100
x (mm) 50
0.07
0
0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 3.5 4
y (mm) 128
0.06
96
64
0.05 32 0
y 0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 3.5 4
EMG(CH1) 0
0.04 10
0.03 –10
0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 3.5 4
EMG(CH2) 0
0.02 10
0.01 –10
0.03 0.04 0.05 0.06 0.07 0.08 0.09 0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 3.5 4
(A) x (B) Time (s)
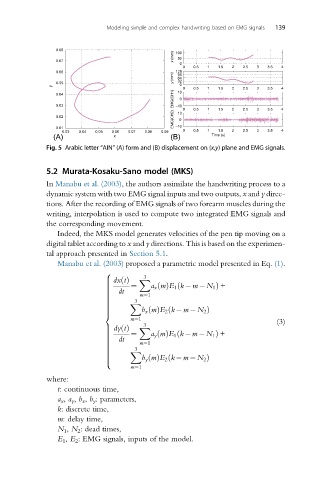
Fig. 5 Arabic letter “AIN” (A) form and (B) displacement on (x,y) plane and EMG signals.
5.2 Murata-Kosaku-Sano model (MKS)
In Manabu et al. (2003), the authors assimilate the handwriting process to a
dynamic system with two EMG signal inputs and two outputs, x and y direc-
tions. After the recording of EMG signals of two forearm muscles during the
writing, interpolation is used to compute two integrated EMG signals and
the corresponding movement.
Indeed, the MKS model generates velocities of the pen tip moving on a
digital tablet according to x and y directions. This is based on the experimen-
tal approach presented in Section 5.1.
Manabu et al. (2003) proposed a parametric model presented in Eq. (1).
8
3
dx tðÞ X
>
>
ð
> ¼ a x mðÞE 1 k m N 1 Þ +
>
> dt
m¼1
>
>
>
3
>
>
X
>
>
ð
> b x mðÞE 2 k m N 2 Þ
>
<
m¼1 (3)
3
dy tðÞ X
>
>
ð
> ¼ a y mðÞE 1 k m N 1 Þ +
>
dt
>
>
> m¼1
>
3
>
>
X
>
>
ð
> b y mðÞE 2 k m N 2 Þ
>
:
m¼1
where:
t: continuous time,
a x , a y , b x , b y : parameters,
k: discrete time,
m: delay time,
N 1 , N 2 : dead times,
E 1 , E 2 : EMG signals, inputs of the model.