Page 16 - Control Theory in Biomedical Engineering
P. 16
Modeling and control in physiology 5
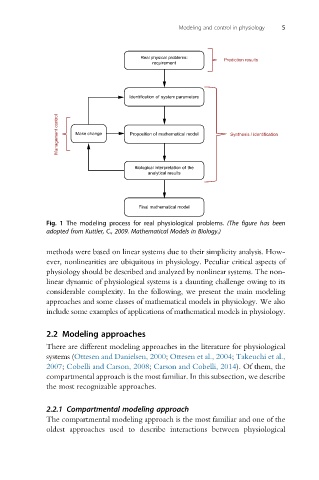
Real physical problems: Prediction results
requirement
Identification of system parameters
Management control Make change Proposition of mathematical model Synthesis / identification
Biological interpretation of the
analytical results
Final mathematical model
Fig. 1 The modeling process for real physiological problems. (The figure has been
adopted from Kuttler, C., 2009. Mathematical Models in Biology.)
methods were based on linear systems due to their simplicity analysis. How-
ever, nonlinearities are ubiquitous in physiology. Peculiar critical aspects of
physiology should be described and analyzed by nonlinear systems. The non-
linear dynamic of physiological systems is a daunting challenge owing to its
considerable complexity. In the following, we present the main modeling
approaches and some classes of mathematical models in physiology. We also
include some examples of applications of mathematical models in physiology.
2.2 Modeling approaches
There are different modeling approaches in the literature for physiological
systems (Ottesen and Danielsen, 2000; Ottesen et al., 2004; Takeuchi et al.,
2007; Cobelli and Carson, 2008; Carson and Cobelli, 2014). Of them, the
compartmental approach is the most familiar. In this subsection, we describe
the most recognizable approaches.
2.2.1 Compartmental modeling approach
The compartmental modeling approach is the most familiar and one of the
oldest approaches used to describe interactions between physiological