Page 21 - Control Theory in Biomedical Engineering
P. 21
Modeling and control in physiology 9
Pout, Qout
Vessel
R L
Pin Pout
C
Pin, Qin
Qin Qout
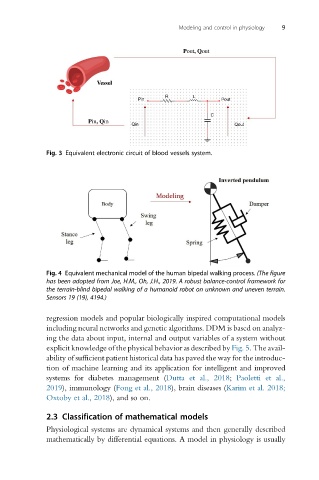
Fig. 3 Equivalent electronic circuit of blood vessels system.
Fig. 4 Equivalent mechanical model of the human bipedal walking process. (The figure
has been adopted from Joe, H.M., Oh, J.H., 2019. A robust balance-control framework for
the terrain-blind bipedal walking of a humanoid robot on unknown and uneven terrain.
Sensors 19 (19), 4194.)
regression models and popular biologically inspired computational models
including neural networks and genetic algorithms. DDM is based on analyz-
ing the data about input, internal and output variables of a system without
explicit knowledge of the physical behavior as described by Fig. 5. The avail-
ability of sufficient patient historical data has paved the way for the introduc-
tion of machine learning and its application for intelligent and improved
systems for diabetes management (Dutta et al., 2018; Paoletti et al.,
2019), immunology (Fong et al., 2018), brain diseases (Karim et al. 2018;
Oxtoby et al., 2018), and so on.
2.3 Classification of mathematical models
Physiological systems are dynamical systems and then generally described
mathematically by differential equations. A model in physiology is usually