Page 25 - Control Theory in Biomedical Engineering
P. 25
Modeling and control in physiology 13
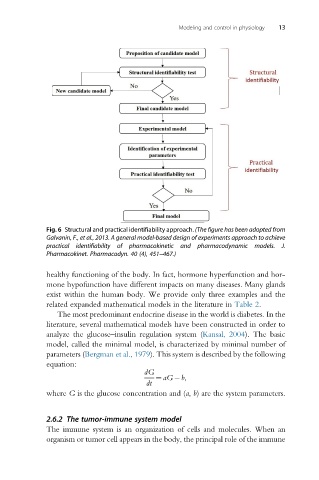
Fig. 6 Structural and practical identifiability approach. (The figure has been adopted from
Galvanin, F., et al., 2013. A general model-based design of experiments approach to achieve
practical identifiability of pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic models. J.
Pharmacokinet. Pharmacodyn. 40 (4), 451–467.)
healthy functioning of the body. In fact, hormone hyperfunction and hor-
mone hypofunction have different impacts on many diseases. Many glands
exist within the human body. We provide only three examples and the
related expanded mathematical models in the literature in Table 2.
The most predominant endocrine disease in the world is diabetes. In the
literature, several mathematical models have been constructed in order to
analyze the glucose–insulin regulation system (Kansal, 2004). The basic
model, called the minimal model, is characterized by minimal number of
parameters (Bergman et al., 1979). This system is described by the following
equation:
dG
¼ aG b,
dt
where G is the glucose concentration and (a, b) are the system parameters.
2.6.2 The tumor-immune system model
The immune system is an organization of cells and molecules. When an
organism or tumor cell appears in the body, the principal role of the immune