Page 370 - Corrosion Engineering Principles and Practice
P. 370
338 C h a p t e r 9 A t m o s p h e r i c C o r r o s i o n 339
In absence of any particular surface effects, the dew point
corresponds to the temperature at which condensation occurs. A high
RH would therefore be associated with a dew point close to the current
air temperature. If the RH was 100 percent, for example, the dew point
would be equal to the current temperature. Given a constant dew point,
an increase in temperature will lead to a decrease in relative humidity.
Equation (9.3) provides a convenient way to calculate the dew point as
a function of temperature to within ±0.4°C [6]:
At
B ln RH +
+
t = B t (9.3)
d
−
A ln RH − At
+
B t
where A = 17.625
B = 243.04°C
RH is the relative humidity as a fraction (not percent)
t is the surface temperature (°C)
t is the dew point temperature (°C)
d
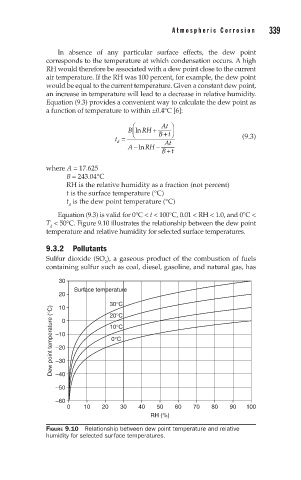
Equation (9.3) is valid for 0°C < t < 100°C, 0.01 < RH < 1.0, and 0°C <
T < 50°C. Figure 9.10 illustrates the relationship between the dew point
d
temperature and relative humidity for selected surface temperatures.
9.3.2 Pollutants
Sulfur dioxide (SO ), a gaseous product of the combustion of fuels
2
containing sulfur such as coal, diesel, gasoline, and natural gas, has
30
Surface temperature
20
30°C
10
Dew point temperature (°C) –10 10°C
20°C
0
0°C
–20
–30
–40
–50
–60
0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100
RH (%)
FIGURE 9.10 Relationship between dew point temperature and relative
humidity for selected surface temperatures.