Page 441 - Corrosion Engineering Principles and Practice
P. 441
410 C h a p t e r 1 0 C o r r o s i o n i n S o i l s a n d M i c r o b i o l o g i c a l l y I n f l u e n c e d C o r r o s i o n 411
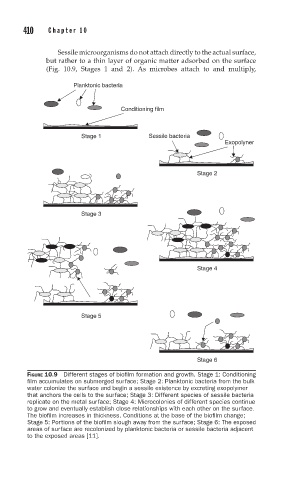
Sessile microorganisms do not attach directly to the actual surface,
but rather to a thin layer of organic matter adsorbed on the surface
(Fig. 10.9, Stages 1 and 2). As microbes attach to and multiply,
Planktonic bacteria
Conditioning film
Stage 1 Sessile bacteria
Exopolyner
Stage 2
Stage 3
Stage 4
Stage 5
Stage 6
FIGURE 10.9 Different stages of biofilm formation and growth. Stage 1: Conditioning
film accumulates on submerged surface; Stage 2: Planktonic bacteria from the bulk
water colonize the surface and begin a sessile existence by excreting exopolymer
that anchors the cells to the surface; Stage 3: Different species of sessile bacteria
replicate on the metal surface; Stage 4: Microcolonies of different species continue
to grow and eventually establish close relationships with each other on the surface.
The biofilm increases in thickness. Conditions at the base of the biofilm change;
Stage 5: Portions of the biofilm slough away from the surface; Stage 6: The exposed
areas of surface are recolonized by planktonic bacteria or sessile bacteria adjacent
to the exposed areas [11].