Page 486 - Corrosion Engineering Principles and Practice
P. 486
452 C h a p t e r 1 1 M a t e r i a l s S e l e c t i o n , Te s t i n g , a n d D e s i g n C o n s i d e r a t i o n s 453
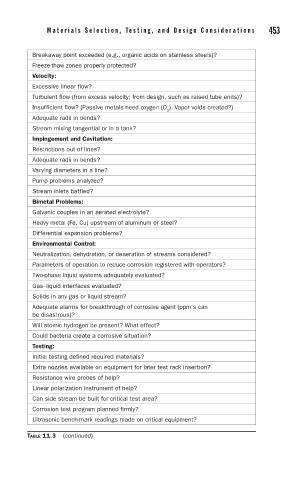
Breakaway point exceeded (e.g., organic acids on stainless steels)?
Freeze-thaw zones properly protected?
Velocity:
Excessive linear flow?
Turbulent flow (from excess velocity; from design, such as raised tube ends)?
Insufficient flow? (Passive metals need oxygen (O ). Vapor voids created?)
2
Adequate radii in bends?
Stream mixing tangential or in a tank?
Impingement and Cavitation:
Restrictions out of lines?
Adequate radii in bends?
Varying diameters in a line?
Pump problems analyzed?
Stream inlets baffled?
Bimetal Problems:
Galvanic couples in an aerated electrolyte?
Heavy metal (Fe, Cu) upstream of aluminum or steel?
Differential expansion problems?
Environmental Control:
Neutralization, dehydration, or deaeration of streams considered?
Parameters of operation to reduce corrosion registered with operators?
Two-phase liquid systems adequately evaluated?
Gas–liquid interfaces evaluated?
Solids in any gas or liquid stream?
Adequate alarms for breakthrough of corrosive agent (ppm's can
be disastrous)?
Will atomic hydrogen be present? What effect?
Could bacteria create a corrosive situation?
Testing:
Initial testing defined required materials?
Extra nozzles available on equipment for later test rack insertion?
Resistance wire probes of help?
Linear polarization instrument of help?
Can side stream be built for critical test area?
Corrosion test program planned firmly?
Ultrasonic bench-mark readings made on critical equipment?
TABLE 11.3 (continued)