Page 529 - Corrosion Engineering Principles and Practice
P. 529
494 C h a p t e r 1 2 C o r r o s i o n a s a R i s k 495
an analysis what level will be adopted as otherwise some areas may
be examined in greater details than others. If conducted at too deep a
level, FMECA can be time consuming and tedious, but it can also lead
to great understanding of the system.
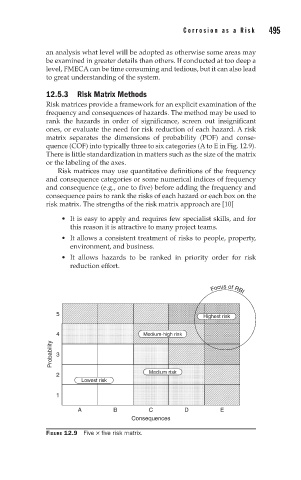
12.5.3 Risk Matrix Methods
Risk matrices provide a framework for an explicit examination of the
frequency and consequences of hazards. The method may be used to
rank the hazards in order of significance, screen out insignificant
ones, or evaluate the need for risk reduction of each hazard. A risk
matrix separates the dimensions of probability (POF) and conse-
quence (COF) into typically three to six categories (A to E in Fig. 12.9).
There is little standardization in matters such as the size of the matrix
or the labeling of the axes.
Risk matrices may use quantitative definitions of the frequency
and consequence categories or some numerical indices of frequency
and consequence (e.g., one to five) before adding the frequency and
consequence pairs to rank the risks of each hazard or each box on the
risk matrix. The strengths of the risk matrix approach are [10]
• It is easy to apply and requires few specialist skills, and for
this reason it is attractive to many project teams.
• It allows a consistent treatment of risks to people, property,
environment, and business.
• It allows hazards to be ranked in priority order for risk
reduction effort.
Focus of RBI
5 Highest risk
4 Medium-high risk
Probability 3
Medium risk
2
Lowest risk
1
A B C D E
Consequences
FIGURE 12.9 Five × five risk matrix.