Page 536 - Corrosion Engineering Principles and Practice
P. 536
502 C h a p t e r 1 2 C o r r o s i o n a s a R i s k 503
0.99998 Probability of not cracking
0.5 Clamp
0.9 Find by inspection
0.2 $ Gas plant
0.3 $ CCU
0.7 Clamp
Find before 0
0.5 leak 0.2499 $ Gas plant
$ CCU
Piping 0.05 Fire
0.7 Autorefrigerate 0.0001 VCE
0.5 Clamp
0 $ Gas plant
0.299 $ CCU
Leak 0.5 Not find 0.2 Fire
0.99 before break 0.001 VCE
0.7 Clamp
0.00002 Probability Find before 0 $ Gas plant
of cracking 0.97 Leak becomes 0.2499 $ CCU
large 0.05 Fire
Not 0.0001 VCE
Do not find 0.3 Autorefrigerate 0.5 Clamp
0.1 by 0 $ Gas plant
inspection 0.299 $ CCU
0.03 Not find 0.2 Fire
0.001 VCE
0.33 Leak/break/no fire
0.6 Leak/break/fire
0.01 Break 0.07 Leak/break/VCE
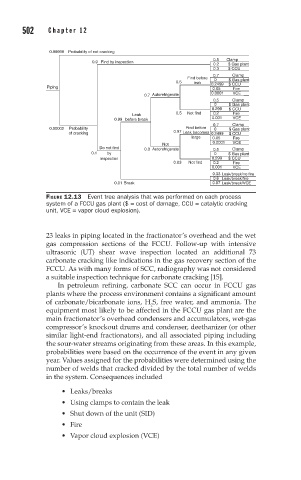
FIGURE 12.13 Event tree analysis that was performed on each process
system of a FCCU gas plant ($ = cost of damage, CCU = catalytic cracking
unit, VCE = vapor cloud explosion).
23 leaks in piping located in the fractionator’s overhead and the wet
gas compression sections of the FCCU. Follow-up with intensive
ultrasonic (UT) shear wave inspection located an additional 73
carbonate cracking like indications in the gas recovery section of the
FCCU. As with many forms of SCC, radiography was not considered
a suitable inspection technique for carbonate cracking [15].
In petroleum refining, carbonate SCC can occur in FCCU gas
plants where the process environment contains a significant amount
of carbonate/bicarbonate ions, H S, free water, and ammonia. The
2
equipment most likely to be affected in the FCCU gas plant are the
main fractionator’s overhead condensers and accumulators, wet-gas
compressor’s knockout drums and condenser, deethanizer (or other
similar light-end fractionators), and all associated piping including
the sour-water streams originating from these areas. In this example,
probabilities were based on the occurrence of the event in any given
year. Values assigned for the probabilities were determined using the
number of welds that cracked divided by the total number of welds
in the system. Consequences included
• Leaks/breaks
• Using clamps to contain the leak
• Shut down of the unit (SID)
• Fire
• Vapor cloud explosion (VCE)