Page 145 - Cultures and Organizations
P. 145
124 DIMENSIONS OF NATIONAL CULTURES
Asked about the effects of the introduction of the Internet, respondents
in the less individualist European countries stressed that people who do
not use the Internet have more time for themselves, their family, and their
friends. 49
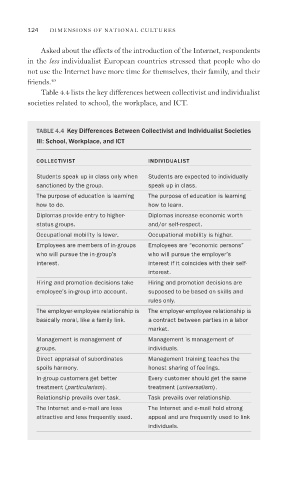
Table 4.4 lists the key differences between collectivist and individualist
societies related to school, the workplace, and ICT.
TABLE 4.4 Key Differences Between Collectivist and Individualist Societies
III: School, Workplace, and ICT
COLLECTIVIST INDIVIDUALIST
Students speak up in class only when Students are expected to individually
sanctioned by the group. speak up in class.
The purpose of education is learning The purpose of education is learning
how to do. how to learn.
Diplomas provide entry to higher- Diplomas increase economic worth
status groups. and/or self-respect.
Occupational mobility is lower. Occupational mobility is higher.
Employees are members of in-groups Employees are “economic persons”
who will pursue the in-group’s who will pursue the employer’s
interest. interest if it coincides with their self-
interest.
Hiring and promotion decisions take Hiring and promotion decisions are
employee’s in-group into account. supposed to be based on skills and
rules only.
The employer-employee relationship is The employer-employee relationship is
basically moral, like a family link. a contract between parties in a labor
market.
Management is management of Management is management of
groups. individuals.
Direct appraisal of subordinates Management training teaches the
spoils harmony. honest sharing of feelings.
In-group customers get better Every customer should get the same
treatment (particularism). treatment (universalism).
Relationship prevails over task. Task prevails over relationship.
The Internet and e-mail are less The Internet and e-mail hold strong
attractive and less frequently used. appeal and are frequently used to link
individuals.