Page 151 - Cultures and Organizations
P. 151
130 DIMENSIONS OF NATIONAL CULTURES
This means that the results of psychological experiments in a collectivist
society depend on whether participants belong to the same in-group.
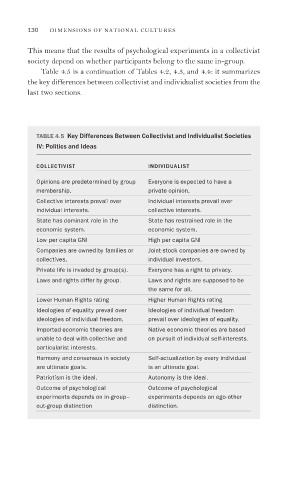
Table 4.5 is a continuation of Tables 4.2, 4.3, and 4.4: it summarizes
the key differences between collectivist and individualist societies from the
last two sections.
TABLE 4.5 Key Differences Between Collectivist and Individualist Societies
IV: Politics and Ideas
COLLECTIVIST INDIVIDUALIST
Opinions are predetermined by group Everyone is expected to have a
membership. private opinion.
Collective interests prevail over Individual interests prevail over
individual interests. collective interests.
State has dominant role in the State has restrained role in the
economic system. economic system.
Low per capita GNI High per capita GNI
Companies are owned by families or Joint-stock companies are owned by
collectives. individual investors.
Private life is invaded by group(s). Everyone has a right to privacy.
Laws and rights differ by group. Laws and rights are supposed to be
the same for all.
Lower Human Rights rating Higher Human Rights rating
Ideologies of equality prevail over Ideologies of individual freedom
ideologies of individual freedom. prevail over ideologies of equality.
Imported economic theories are Native economic theories are based
unable to deal with collective and on pursuit of individual self-interests.
particularist interests.
Harmony and consensus in society Self-actualization by every individual
are ultimate goals. is an ultimate goal.
Patriotism is the ideal. Autonomy is the ideal.
Outcome of psychological Outcome of psychological
experiments depends on in-group– experiments depends on ego-other
out-group distinction distinction.