Page 250 - Cultures and Organizations
P. 250
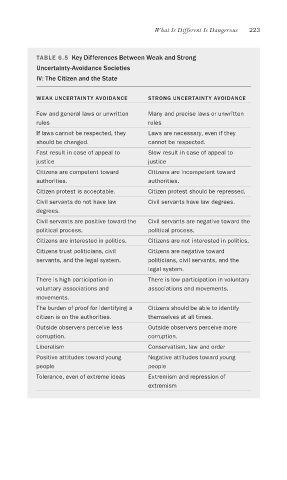
What Is Different Is Dangerous 223
TABLE 6.5 Key Differences Between Weak and Strong
Uncertainty-Avoidance Societies
IV: The Citizen and the State
WEAK UNCERTAINTY AVOIDANCE STRONG UNCERTAINTY AVOIDANCE
Few and general laws or unwritten Many and precise laws or unwritten
rules rules
If laws cannot be respected, they Laws are necessary, even if they
should be changed. cannot be respected.
Fast result in case of appeal to Slow result in case of appeal to
justice justice
Citizens are competent toward Citizens are incompetent toward
authorities. authorities.
Citizen protest is acceptable. Citizen protest should be repressed.
Civil servants do not have law Civil servants have law degrees.
degrees.
Civil servants are positive toward the Civil servants are negative toward the
political process. political process.
Citizens are interested in politics. Citizens are not interested in politics.
Citizens trust politicians, civil Citizens are negative toward
servants, and the legal system. politicians, civil servants, and the
legal system.
There is high participation in There is low participation in voluntary
voluntary associations and associations and movements.
movements.
The burden of proof for identifying a Citizens should be able to identify
citizen is on the authorities. themselves at all times.
Outside observers perceive less Outside observers perceive more
corruption. corruption.
Liberalism Conservatism, law and order
Positive attitudes toward young Negative attitudes toward young
people people
Tolerance, even of extreme ideas Extremism and repression of
extremism