Page 218 - DSP Integrated Circuits
P. 218
5.5 Scaling of Signal Levels 203
ues in the node of interest. This method of computing the L2-norm will be used in
Example 5.6.
Loo-Norm
The Loo-norm corresponds to the maximum value of the magnitude function.
Hence, we have
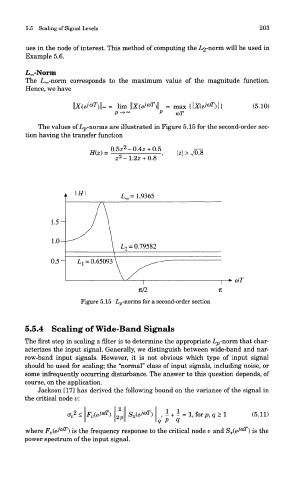
The values of Lp-norms are illustrated in Figure 5.15 for the second-order sec-
tion having the transfer function
Figure 5.15 Lp-norms for a second-order section
5.5.4 Scaling of Wide-Band Signals
The first step in scaling a filter is to determine the appropriate L^-norm that char-
acterizes the input signal. Generally, we distinguish between wide-band and nar-
row-band input signals. However, it is not obvious which type of input signal
should be used for scaling; the "normal" class of input signals, including noise, or
some infrequently occurring disturbance. The answer to this question depends, of
course, on the application.
Jackson [17] has derived the following bound on the variance of the signal in
the critical node v:
a)T 0
where F v(eJ ) is the frequency response to the critical node v and S^eJ ^) is the
power spectrum of the input signal.