Page 228 - DSP Integrated Circuits
P. 228
5.7 Measuring Round-Off Noise 213
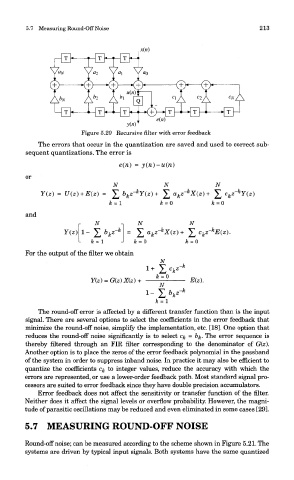
Figure 5.20 Recursive filter with error feedback
The errors that occur in the quantization are saved and used to correct sub-
sequent quantizations. The error is
or
and
For the output of the filter we obtain
The round-off error is affected by a different transfer function than is the input
signal. There are several options to select the coefficients in the error feedback that
minimize the round-off noise, simplify the implementation, etc. [18]. One option that
reduces the round-off noise significantly is to select c& = &&. The error sequence is
thereby filtered through an FIR filter corresponding to the denominator of G(z).
Another option is to place the zeros of the error feedback polynomial in the passband
of the system in order to suppress inband noise. In practice it may also be efficient to
quantize the coefficients c& to integer values, reduce the accuracy with which the
errors are represented, or use a lower-order feedback path. Most standard signal pro-
cessors are suited to error feedback since they have double precision accumulators.
Error feedback does not affect the sensitivity or transfer function of the filter.
Neither does it affect the signal levels or overflow probability. However, the magni-
tude of parasitic oscillations may be reduced and even eliminated in some cases [29].
5.7 MEASURING ROUND-OFF NOISE
Round-off noise; can be measured according to the scheme shown in Figure 5.21. The
systems are driven by typical input signals. Both systems have the same quantized