Page 84 - DSP Integrated Circuits
P. 84
3.8 Signal Processing Systems 69
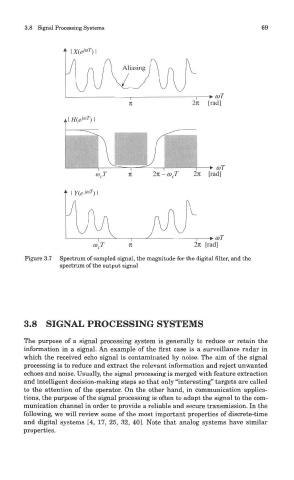
Figure 3.7 Spectrum of sampled signal, the magnitude for the digital filter, and the
spectrum of the output signal
3.8 SIGNAL PROCESSING SYSTEMS
The purpose of a signal processing system is generally to reduce or retain the
information in a signal. An example of the first case is a surveillance radar in
which the received echo signal is contaminated by noise. The aim of the signal
processing is to reduce and extract the relevant information and reject unwanted
echoes and noise. Usually, the signal processing is merged with feature extraction
and intelligent decision-making steps so that only "interesting" targets are called
to the attention of the operator. On the other hand, in communication applica-
tions, the purpose of the signal processing is often to adapt the signal to the com-
munication channel in order to provide a reliable and secure transmission. In the
following, we will review some of the most important properties of discrete-time
and digital systems [4, 17, 25, 32, 40]. Note that analog systems have similar
properties.