Page 126 - Decision Making Applications in Modern Power Systems
P. 126
Power quality issues of smart microgrids Chapter | 4 91
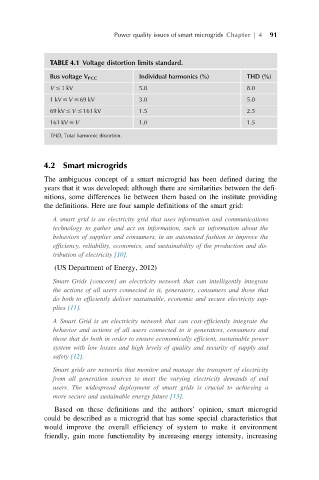
TABLE 4.1 Voltage distortion limits standard.
Bus voltage V PCC Individual harmonics (%) THD (%)
V # 1 kV 5.0 8.0
1kV # V # 69 kV 3.0 5.0
69 kV # V # 161 kV 1.5 2.5
161 kV # V 1.0 1.5
THD, Total harmonic distortion.
4.2 Smart microgrids
The ambiguous concept of a smart microgrid has been defined during the
years that it was developed; although there are similarities between the defi-
nitions, some differences lie between them based on the institute providing
the definitions. Here are four sample definitions of the smart grid:
A smart grid is an electricity grid that uses information and communications
technology to gather and act on information, such as information about the
behaviors of supplier and consumers, in an automated fashion to improve the
efficiency, reliability, economics, and sustainability of the production and dis-
tribution of electricity [10].
(US Department of Energy, 2012)
Smart Grids [concern] an electricity network that can intelligently integrate
the actions of all users connected to it, generators, consumers and those that
do both to efficiently deliver sustainable, economic and secure electricity sup-
plies [11].
A Smart Grid is an electricity network that can cost-efficiently integrate the
behavior and actions of all users connected to it generators, consumers and
those that do both in order to ensure economically efficient, sustainable power
system with low losses and high levels of quality and security of supply and
safety [12].
Smart grids are networks that monitor and manage the transport of electricity
from all generation sources to meet the varying electricity demands of end
users. The widespread deployment of smart grids is crucial to achieving a
more secure and sustainable energy future [13].
Based on these definitions and the authors’ opinion, smart microgrid
could be described as a microgrid that has some special characteristics that
would improve the overall efficiency of system to make it environment
friendly, gain more functionality by increasing energy intensity, increasing