Page 85 - Design for Environment A Guide to Sustainable Product Development
P. 85
64 Cha pte r F o u r
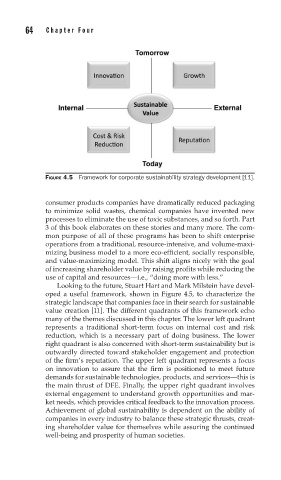
FIGURE 4.5 Framework for corporate sustainability strategy development [11].
consumer products companies have dramatically re duced packaging
to minimize solid wastes, chemical companies have invented new
processes to eliminate the use of toxic substances, and so forth. Part
3 of this book elaborates on these stories and many more. The com-
mon purpose of all of these programs has been to shift enterprise
operations from a traditional, resource-intensive, and volume-maxi-
mizing business model to a more eco-efficient, socially responsible,
and value-maximizing model. This shift aligns nicely with the goal
of increasing shareholder value by raising profits while reducing the
use of capital and resources—i.e., “doing more with less.”
Looking to the future, Stuart Hart and Mark Milstein have devel-
oped a useful framework, shown in Figure 4.5, to characterize the
strategic landscape that companies face in their search for sustainable
value creation [11]. The different quadrants of this framework echo
many of the themes discussed in this chapter. The lower left quadrant
represents a traditional short-term focus on internal cost and risk
reduction, which is a necessary part of doing business. The lower
right quadrant is also concerned with short-term sustainability but is
outwardly directed toward stakeholder engagement and protection
of the firm’s reputation. The upper left quadrant represents a focus
on innovation to assure that the firm is positioned to meet future
demands for sustainable technologies, products, and services—this is
the main thrust of DFE. Finally, the upper right quadrant involves
external engagement to understand growth opportunities and mar-
ket needs, which provides critical feedback to the innovation process.
Achievement of global sustainability is dependent on the ability of
companies in every industry to balance these strategic thrusts, creat-
ing shareholder value for themselves while assuring the continued
well-being and prosperity of human societies.