Page 160 - Design for Six Sigma a Roadmap for Product Development
P. 160
134 Chapter Five
internal company requirements. The emphasis here is placed on foster-
ing deeper understanding of customers by enabling all design team
members to learn by experiencing meaningful, direct engagements
with customers.
Direct engagement with external and internal customers helps the
DFSS team in interpreting customer satisfaction success parameters
in increasing detail as the project progresses, thereby providing an
ongoing reality check to help reduce expensive downstream design
changes, scrap, and rework, thus avoiding the design hidden factory
altogether. This direct engagement with customers will foster creativ-
ity and innovation, leading to unprecedented customer products.
The understanding of customer wants, needs, delights, and usage
profiles; operating conditions; and environmental issues gives the
DFSS team the information needed to design universal solutions.
These overall attributes are called the “WHATs” array and will be
referred to as such in discussion of the quality function deployment
(QFD) methodology. The WHATs array is housed in the left room of the
“house of quality” matrix of the QFD (see Chap. 7). Traditional design
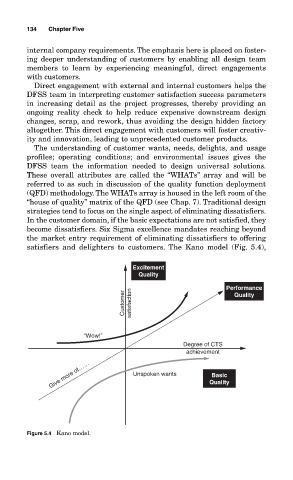
strategies tend to focus on the single aspect of eliminating dissatisfiers.
In the customer domain, if the basic expectations are not satisfied, they
become dissatisfiers. Six Sigma excellence mandates reaching beyond
the market entry requirement of eliminating dissatisfiers to offering
satisfiers and delighters to customers. The Kano model (Fig. 5.4),
Excitement
Quality
Performance
Customer satisfaction
Quality
“Wow!”
Degree of CTS
achievement
Give more of…… Unspoken wants Quality
Basic
Figure 5.4 Kano model.