Page 199 - Design for Six Sigma a Roadmap for Product Development
P. 199
172 Chapter Five
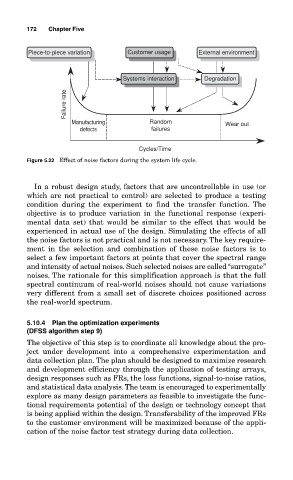
Piece-to-piece variation Customer usage External environment
Systems interaction Degradation
Failure rate
Manufacturing Random Wear out
defects failures
Cycles/Time
Figure 5.22 Effect of noise factors during the system life cycle.
In a robust design study, factors that are uncontrollable in use (or
which are not practical to control) are selected to produce a testing
condition during the experiment to find the transfer function. The
objective is to produce variation in the functional response (experi-
mental data set) that would be similar to the effect that would be
experienced in actual use of the design. Simulating the effects of all
the noise factors is not practical and is not necessary. The key require-
ment in the selection and combination of these noise factors is to
select a few important factors at points that cover the spectral range
and intensity of actual noises. Such selected noises are called “surrogate”
noises. The rationale for this simplification approach is that the full
spectral continuum of real-world noises should not cause variations
very different from a small set of discrete choices positioned across
the real-world spectrum.
5.10.4 Plan the optimization experiments
(DFSS algorithm step 9)
The objective of this step is to coordinate all knowledge about the pro-
ject under development into a comprehensive experimentation and
data collection plan. The plan should be designed to maximize research
and development efficiency through the application of testing arrays,
design responses such as FRs, the loss functions, signal-to-noise ratios,
and statistical data analysis. The team is encouraged to experimentally
explore as many design parameters as feasible to investigate the func-
tional requirements potential of the design or technology concept that
is being applied within the design. Transferability of the improved FRs
to the customer environment will be maximized because of the appli-
cation of the noise factor test strategy during data collection.