Page 198 - Design for Six Sigma a Roadmap for Product Development
P. 198
Design for Six Sigma Project Algorithm 171
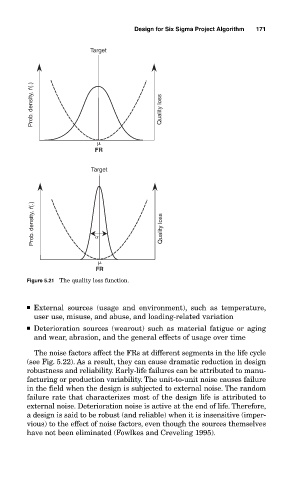
Target
Prob. density, f (.) Quality loss
FR
Target
Prob. density, f(.) Quality loss
FR
Figure 5.21 The quality loss function.
■ External sources (usage and environment), such as temperature,
user use, misuse, and abuse, and loading-related variation
■ Deterioration sources (wearout) such as material fatigue or aging
and wear, abrasion, and the general effects of usage over time
The noise factors affect the FRs at different segments in the life cycle
(see Fig. 5.22). As a result, they can cause dramatic reduction in design
robustness and reliability. Early-life failures can be attributed to manu-
facturing or production variability. The unit-to-unit noise causes failure
in the field when the design is subjected to external noise. The random
failure rate that characterizes most of the design life is attributed to
external noise. Deterioration noise is active at the end of life. Therefore,
a design is said to be robust (and reliable) when it is insensitive (imper-
vious) to the effect of noise factors, even though the sources themselves
have not been eliminated (Fowlkes and Creveling 1995).