Page 193 - Design for Six Sigma a Roadmap for Product Development
P. 193
166 Chapter Five
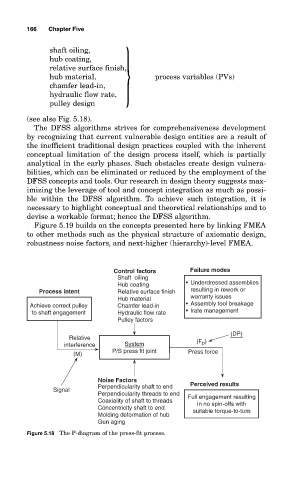
shaft oiling,
hub coating,
relative surface finish, }
hub material, process variables (PVs)
chamfer lead-in,
hydraulic flow rate,
pulley design
(see also Fig. 5.18).
The DFSS algorithms strives for comprehensiveness development
by recognizing that current vulnerable design entities are a result of
the inefficient traditional design practices coupled with the inherent
conceptual limitation of the design process itself, which is partially
analytical in the early phases. Such obstacles create design vulnera-
bilities, which can be eliminated or reduced by the employment of the
DFSS concepts and tools. Our research in design theory suggests max-
imizing the leverage of tool and concept integration as much as possi-
ble within the DFSS algorithm. To achieve such integration, it is
necessary to highlight conceptual and theoretical relationships and to
devise a workable format; hence the DFSS algorithm.
Figure 5.19 builds on the concepts presented here by linking FMEA
to other methods such as the physical structure of axiomatic design,
robustness noise factors, and next-higher (hierarchy)-level FMEA.
Control factors Failure modes
Shaft oiling
Hub coating • Underdressed assemblies
Process intent Relative surface finish resulting in rework or
Hub material warranty issues
Achieve correct pulley Chamfer lead-in • Assembly tool breakage
to shaft engagement Hydraulic flow rate • Irate management
Pulley factors
(DP)
Relative (F p )
interference System
P/S press fit joint Press force
(M)
Noise Factors
Perpendicularity shaft to end Perceived results
Signal
Perpendicularity threads to end Full engagement resulting
Coaxiality of shaft to threads in no spin-offs with
Concentricity shaft to end suitable torque-to-turn
Molding deformation of hub
Gun aging
Figure 5.18 The P-diagram of the press-fit process.