Page 181 - Design for Six Sigma for Service (Six SIGMA Operational Methods)
P. 181
Value Engineering 153
Minor primary path
How Why
Independent Dependent
function
function
(supporting)
Objectives
or
specifications
Highest-order Basic Dependent Lowest-
functions order function
function function
(output) (input)
Major primary path
Activity
When
Scope of the project
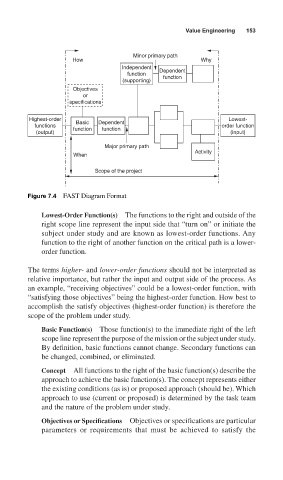
Figure 7.4 FAST Diagram Format
Lowest-Order Function(s) The functions to the right and outside of the
right scope line represent the input side that “turn on” or initiate the
subject under study and are known as lowest-order functions. Any
function to the right of another function on the critical path is a lower-
order function.
The terms higher- and lower-order functions should not be interpreted as
relative importance, but rather the input and output side of the process. As
an example, “receiving objectives” could be a lowest-order function, with
“satisfying those objectives” being the highest-order function. How best to
accomplish the satisfy objectives (highest-order function) is therefore the
scope of the problem under study.
Basic Function(s) Those function(s) to the immediate right of the left
scope line represent the purpose of the mission or the subject under study.
By definition, basic functions cannot change. Secondary functions can
be changed, combined, or eliminated.
Concept All functions to the right of the basic function(s) describe the
approach to achieve the basic function(s). The concept represents either
the existing conditions (as is) or proposed approach (should be). Which
approach to use (current or proposed) is determined by the task team
and the nature of the problem under study.
Objectives or Specifications Objectives or specifications are particular
parameters or requirements that must be achieved to satisfy the