Page 467 - Design for Six Sigma for Service (Six SIGMA Operational Methods)
P. 467
Theory of Constraints 425
The theory of constraints also believes that the balanced capacity may not
be a good approach for maintaining high throughput. The most important
issue is to balance flow. This is illustrated by Example 12.4.
Example 12.4: Capacity Balance versus Flow Balance
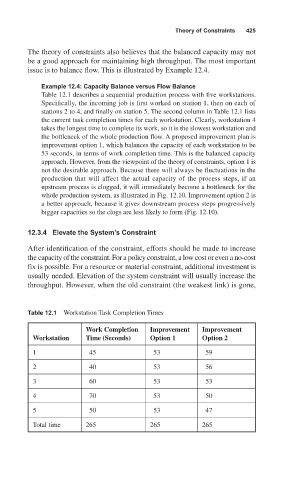
Table 12.1 describes a sequential production process with five workstations.
Specifically, the incoming job is first worked on station 1, then on each of
stations 2 to 4, and finally on station 5. The second column in Table 12.1 lists
the current task completion times for each workstation. Clearly, workstation 4
takes the longest time to complete its work, so it is the slowest workstation and
the bottleneck of the whole production flow. A proposed improvement plan is
improvement option 1, which balances the capacity of each workstation to be
53 seconds, in terms of work completion time. This is the balanced capacity
approach. However, from the viewpoint of the theory of constraints, option 1 is
not the desirable approach. Because there will always be fluctuations in the
production that will affect the actual capacity of the process steps, if an
upstream process is clogged, it will immediately become a bottleneck for the
whole production system, as illustrated in Fig. 12.10. Improvement option 2 is
a better approach, because it gives downstream process steps progressively
bigger capacities so the clogs are less likely to form (Fig. 12.10).
12.3.4 Elevate the System’s Constraint
After identification of the constraint, efforts should be made to increase
the capacity of the constraint. For a policy constraint, a low cost or even a no-cost
fix is possible. For a resource or material constraint, additional investment is
usually needed. Elevation of the system constraint will usually increase the
throughput. However, when the old constraint (the weakest link) is gone,
Table 12.1 Workstation Task Completion Times
Work Completion Improvement Improvement
Workstation Time (Seconds) Option 1 Option 2
1 45 53 59
2 40 53 56
3 60 53 53
4 70 53 50
5 50 53 47
Total time 265 265 265