Page 84 - Design of Reinforced Masonry Structures
P. 84
MASONRY UNITS: APPLICATIONS, TYPES, SIZES, AND CLASSIFICATION 2.37
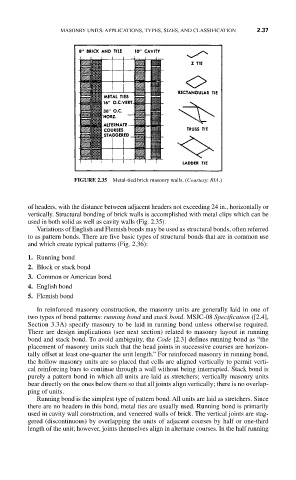
FIGURE 2.35 Metal-tied brick masonry walls. (Courtesy: BIA.)
of headers, with the distance between adjacent headers not exceeding 24 in., horizontally or
vertically. Structural bonding of brick walls is accomplished with metal clips which can be
used in both solid as well as cavity walls (Fig. 2.35).
Variations of English and Flemish bonds may be used as structural bonds, often referred
to as pattern bonds. There are five basic types of structural bonds that are in common use
and which create typical patterns (Fig. 2.36):
1. Running bond
2. Block or stack bond
3. Common or American bond
4. English bond
5. Flemish bond
In reinforced masonry construction, the masonry units are generally laid in one of
two types of bond patterns: running bond and stack bond. MSJC-08 Specification ([2.4],
Section 3.3A) specify masonry to be laid in running bond unless otherwise required.
There are design implications (see next section) related to masonry layout in running
bond and stack bond. To avoid ambiguity, the Code [2.3] defines running bond as “the
placement of masonry units such that the head joints in successive courses are horizon-
tally offset at least one-quarter the unit length.” For reinforced masonry in running bond,
the hollow masonry units are so placed that cells are aligned vertically to permit verti-
cal reinforcing bars to continue through a wall without being interrupted. Stack bond is
purely a pattern bond in which all units are laid as stretchers; vertically masonry units
bear directly on the ones below them so that all joints align vertically; there is no overlap-
ping of units.
Running bond is the simplest type of pattern bond. All units are laid as stretchers. Since
there are no headers in this bond, metal ties are usually used. Running bond is primarily
used in cavity wall construction, and veneered walls of brick. The vertical joints are stag-
gered (discontinuous) by overlapping the units of adjacent courses by half or one-third
length of the unit; however, joints themselves align in alternate courses. In the half running