Page 257 - Design of Simple and Robust Process Plants
P. 257
6.4 Application of Reliability Studies for a Process and Utility Plant 243
Case 3 Case4
100 t/hr
Boil 1
253 t/hr
100 t/hr New
Boil 2 boiler 253 t/hr
253 t/hr
150 t/hr New
boiler
New 253 t/hr
boiler
253 t/hr
150 t/hr New
boiler
New
boiler 253 t/hr
253 t/hr
150 t/hr New
boiler
New
boiler
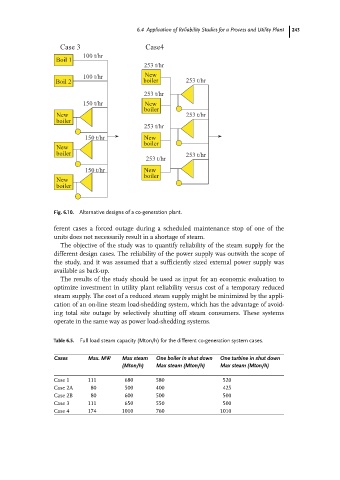
Fig. 6.10. Alternative designs of a co-generation plant.
ferent cases a forced outage during a scheduled maintenance stop of one of the
units does not necessarily result in a shortage of steam.
The objective of the study was to quantify reliability of the steam supply for the
different design cases. The reliability of the power supply was outwith the scope of
the study, and it was assumed that a sufficiently sized external power supply was
available as back-up.
The results of the study should be used as input for an economic evaluation to
optimize investment in utility plant reliability versus cost of a temporary reduced
steam supply. The cost of a reduced steam supply might be minimized by the appli-
cation of an on-line steam load-shedding system, which has the advantage of avoid-
ing total site outage by selectively shutting off steam consumers. These systems
operate in the same way as power load-shedding systems.
Table 6.5. Full load steam capacity (Mton/h) for the different co-generation system cases.
Cases Max. MW Max steam One boiler in shut down One turbine in shut down
(Mton/h) Max steam (Mton/h) Max steam (Mton/h)
Case 1 111 680 580 520
Case 2A 80 500 400 425
Case 2B 80 600 500 500
Case 3 111 650 550 500
Case 4 174 1010 760 1010