Page 258 - Design of Simple and Robust Process Plants
P. 258
244 Chapter 6 Process Design Based on Reliability
The reliability study is approached somewhat differently to that for a process plant.
Utility plants are designed and operated to provide their an ongoing service, at a
certain level. Therefore, the mission time is set at one year (not between turn-
arounds), while shutdowns for maintenance are scheduled over the year without
interruption of the supply. These shutdowns ± called scheduled outages ± must be
incorporated in the reliability approach.
The collection of reliability data is an essential step, and the failure data and sched-
uled outages and forced outage data are summarized in Table 6.6. The failure data of
gas turbines includes the generator, WHB, and the feed supplies. The failure data for
the boilers includes the steam letdown stations and feed water supplies. Steam tur-
bine failure rates were not included as the system was provided with de-superheaters
for bypass operation. The scheduled outages for the frame 6 gas turbines were expli-
citly higher than from LM 2500 turbines, as these require longer overhaul times.
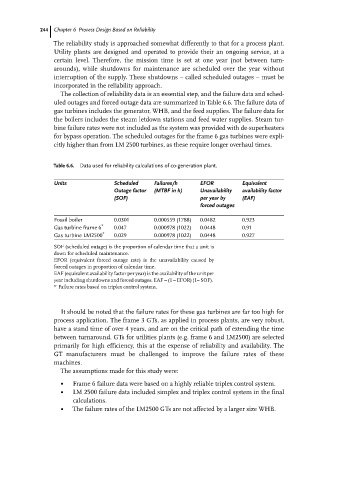
Table 6.6. Data used for reliability calculations of co-generation plant.
Units Scheduled Failures/h EFOR Equivalent
Outage factor (MTBF in h) Unavailability availability factor
(SOF) per year by (EAF)
forced outages
Fossil boiler 0.0301 0.000559 (1788) 0.04820.923
Gas turbine frame 6 * 0.047 0.000978 (1022) 0.0448 0.91
Gas turbine LM2500 * 0.029 0.000978 (1022) 0.0448 0.927
SOF (scheduled outage) is the proportion of calendar time that a unit is
down for scheduled maintenance.
EFOR (equivalent forced outage rate) is the unavailability caused by
forced outages in proportion of calendar time.
EAF (equivalent availability factor per year) is the availability of the unit per
year including shutdowns and forced outages. EAF = (1 ± EFOR) (1± SOF).
* Failure rates based on triplex control system.
It should be noted that the failure rates for these gas turbines are far too high for
process application. The frame 3 GTs, as applied in process plants, are very robust,
have a stand time of over 4 years, and are on the critical path of extending the time
between turnaround. GTs for utilities plants (e.g. frame 6 and LM2500) are selected
primarily for high efficiency, this at the expense of reliability and availability. The
GT manufacturers must be challenged to improve the failure rates of these
machines.
The assumptions made for this study were:
. Frame 6 failure data were based on a highly reliable triplex control system.
. LM 2500 failure data included simplex and triplex control system in the final
calculations.
. The failure rates of the LM2500 GTs are not affected by a larger size WHB.