Page 418 - Design of Simple and Robust Process Plants
P. 418
9.7 Pragmatic Approach to Operation Optimization 405
Note: parameters that need a regular update can only be updated within a closed
loop environment. Such a situation always may force the project to an H level.
The added value for the above-mentioned steps needs to be determined for the
specific situation. This will always remain difficult, for example in off-line optimiza-
tion. You cannot have a good idea of how far you currently operate from the opti-
mum if the optimum is not known! It is the author's experience that the first off-
line optimization results tell you a lot. At first, it tells you where the operational
region for optimum operation lies, and it also focuses attention on the constraints.
The spin-off will be that it is quite easy to calculate the achievable savings of poten-
tial removal of hard constraints.
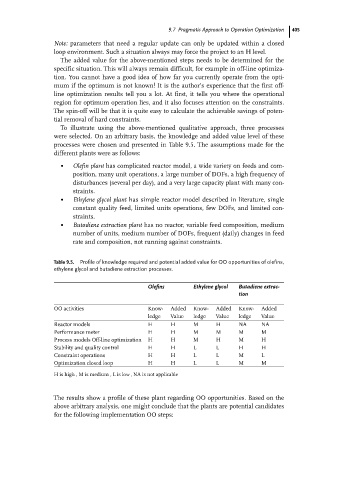
To illustrate using the above-mentioned qualitative approach, three processes
were selected. On an arbitrary basis, the knowledge and added value level of these
processes were chosen and presented in Table 9.5. The assumptions made for the
different plants were as follows:
. Olefin plant has complicated reactor model, a wide variety on feeds and com-
position, many unit operations, a large number of DOFs, a high frequency of
disturbances (several per day), and a very large capacity plant with many con-
straints.
. Ethylene glycol plant has simple reactor model described in literature, single
constant quality feed, limited units operations, few DOFs, and limited con-
straints.
. Butadiene extraction plant has no reactor, variable feed composition, medium
number of units, medium number of DOFs, frequent (daily)changes in feed
rate and composition, not running against constraints.
Table 9.5. Profile of knowledge required and potential added value for OO opportunities of olefins,
ethylene glycol and butadiene extraction processes.
Olefins Ethylene glycol Butadiene extrac-
tion
OO activities Know- Added Know- Added Know- Added
ledge Value ledge Value ledge Value
Reactor models H H M H NA NA
Performance meter H H M M M M
Process models Off-line optimization H H M H M H
Stability and quality control H H L L H H
Constraint operations H H L L M L
Optimization closed loop H H L L M M
H is high , M is medium , L is low , NA is not applicable
The results show a profile of these plant regarding OO opportunities. Based on the
above arbitrary analysis, one might conclude that the plants are potential candidates
for the following implementation OO steps: