Page 121 - Design of Solar Thermal Power Plants
P. 121
2.9 MEASURING INSTRUMENT 107
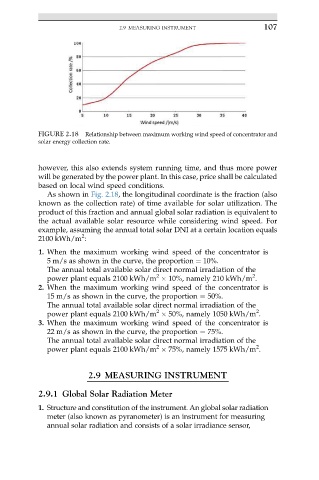
FIGURE 2.18 Relationship between maximum working wind speed of concentrator and
solar energy collection rate.
however, this also extends system running time, and thus more power
will be generated by the power plant. In this case, price shall be calculated
based on local wind speed conditions.
As shown in Fig. 2.18, the longitudinal coordinate is the fraction (also
known as the collection rate) of time available for solar utilization. The
product of this fraction and annual global solar radiation is equivalent to
the actual available solar resource while considering wind speed. For
example, assuming the annual total solar DNI at a certain location equals
2
2100 kWh/m :
1. When the maximum working wind speed of the concentrator is
5 m/s as shown in the curve, the proportion ¼ 10%.
The annual total available solar direct normal irradiation of the
2
2
power plant equals 2100 kWh/m 10%, namely 210 kWh/m .
2. When the maximum working wind speed of the concentrator is
15 m/s as shown in the curve, the proportion ¼ 50%.
The annual total available solar direct normal irradiation of the
2
2
power plant equals 2100 kWh/m 50%, namely 1050 kWh/m .
3. When the maximum working wind speed of the concentrator is
22 m/s as shown in the curve, the proportion ¼ 75%.
The annual total available solar direct normal irradiation of the
2
2
power plant equals 2100 kWh/m 75%, namely 1575 kWh/m .
2.9 MEASURING INSTRUMENT
2.9.1 Global Solar Radiation Meter
1. Structure and constitution of the instrument. An global solar radiation
meter (also known as pyranometer) is an instrument for measuring
annual solar radiation and consists of a solar irradiance sensor,