Page 125 - Design of Solar Thermal Power Plants
P. 125
2.9 MEASURING INSTRUMENT 111
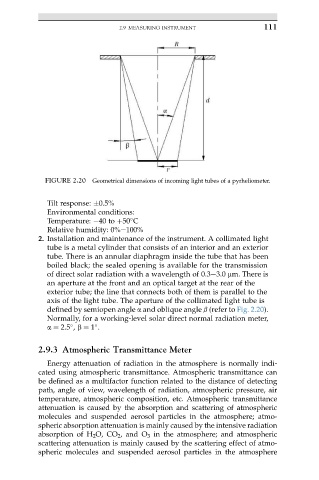
FIGURE 2.20 Geometrical dimensions of incoming light tubes of a pyrheliometer.
Tilt response: 0.5%
Environmental conditions:
Temperature: 40 to þ50 C
Relative humidity: 0%e100%
2. Installation and maintenance of the instrument. A collimated light
tube is a metal cylinder that consists of an interior and an exterior
tube. There is an annular diaphragm inside the tube that has been
boiled black; the sealed opening is available for the transmission
of direct solar radiation with a wavelength of 0.3e3.0 mm. There is
an aperture at the front and an optical target at the rear of the
exterior tube; the line that connects both of them is parallel to the
axis of the light tube. The aperture of the collimated light tube is
defined by semiopen angle a and oblique angle b (refer to Fig. 2.20).
Normally, for a working-level solar direct normal radiation meter,
a ¼ 2.5 , b ¼ 1 .
2.9.3 Atmospheric Transmittance Meter
Energy attenuation of radiation in the atmosphere is normally indi-
cated using atmospheric transmittance. Atmospheric transmittance can
be defined as a multifactor function related to the distance of detecting
path, angle of view, wavelength of radiation, atmospheric pressure, air
temperature, atmospheric composition, etc. Atmospheric transmittance
attenuation is caused by the absorption and scattering of atmospheric
molecules and suspended aerosol particles in the atmosphere; atmo-
spheric absorption attenuation is mainly caused by the intensive radiation
absorption of H 2 O, CO 2 , and O 3 in the atmosphere; and atmospheric
scattering attenuation is mainly caused by the scattering effect of atmo-
spheric molecules and suspended aerosol particles in the atmosphere