Page 214 - Design of Solar Thermal Power Plants
P. 214
198 3. GENERAL DESIGN OF A SOLAR THERMAL POWER PLANT
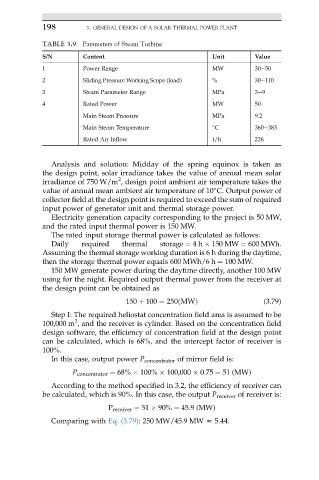
TABLE 3.9 Parameters of Steam Turbine
S/N Content Unit Value
1 Power Range MW 30e50
2 Sliding Pressure Working Scope (load) % 30e110
3 Steam Parameter Range MPa 3e9
4 Rated Power MW 50
Main Steam Pressure MPa 9.2
Main Steam Temperature C 360e383
Rated Air Inflow t/h 226
Analysis and solution: Midday of the spring equinox is taken as
the design point, solar irradiance takes the value of annual mean solar
2
irradiance of 750 W/m , design point ambient air temperature takes the
value of annual mean ambient air temperature of 10 C. Output power of
collector field at the design point is required to exceed the sum of required
input power of generator unit and thermal storage power.
Electricity generation capacity corresponding to the project is 50 MW,
and the rated input thermal power is 150 MW.
The rated input storage thermal power is calculated as follows:
Daily required thermal storage ¼ 4h 150 MW ¼ 600 MWh.
Assuming the thermal storage working duration is 6 h during the daytime,
then the storage thermal power equals 600 MWh/6 h ¼ 100 MW.
150 MW generate power during the daytime directly, another 100 MW
using for the night. Required output thermal power from the receiver at
the design point can be obtained as
150 þ 100 ¼ 250ðMWÞ (3.79)
Step I: The required heliostat concentration field area is assumed to be
2
100,000 m , and the receiver is cylinder. Based on the concentration field
design software, the efficiency of concentration field at the design point
can be calculated, which is 68%, and the intercept factor of receiver is
100%.
In this case, output power P concentrator of mirror field is:
P concentrator ¼ 68% 100% 100,000 0.75 ¼ 51 (MW)
According to the method specified in 3.2, the efficiency of receiver can
be calculated, which is 90%. In this case, the output P receiver of receiver is:
P receiver ¼ 51 90% ¼ 45.9 (MW)
Comparing with Eq. (3.79): 250 MW/45.9 MW z 5.44.