Page 262 - Design of Solar Thermal Power Plants
P. 262
4.3 DESIGN OF THE SOLAR TOWER POWER PLANT 245
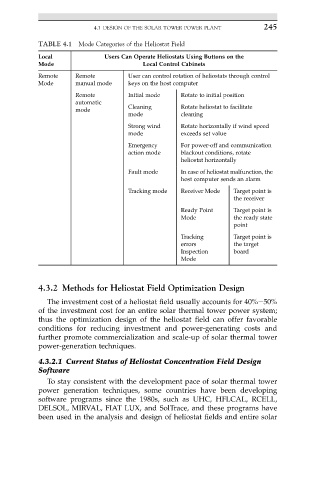
TABLE 4.1 Mode Categories of the Heliostat Field
Local Users Can Operate Heliostats Using Buttons on the
Mode Local Control Cabinets
Remote Remote User can control rotation of heliostats through control
Mode manual mode keys on the host computer
Remote Initial mode Rotate to initial position
automatic
mode Cleaning Rotate heliostat to facilitate
mode cleaning
Strong wind Rotate horizontally if wind speed
mode exceeds set value
Emergency For power-off and communication
action mode blackout conditions, rotate
heliostat horizontally
Fault mode In case of heliostat malfunction, the
host computer sends an alarm
Tracking mode Receiver Mode Target point is
the receiver
Ready Point Target point is
Mode the ready state
point
Tracking Target point is
errors the target
Inspection board
Mode
4.3.2 Methods for Heliostat Field Optimization Design
The investment cost of a heliostat field usually accounts for 40%e50%
of the investment cost for an entire solar thermal tower power system;
thus the optimization design of the heliostat field can offer favorable
conditions for reducing investment and power-generating costs and
further promote commercialization and scale-up of solar thermal tower
power-generation techniques.
4.3.2.1 Current Status of Heliostat Concentration Field Design
Software
To stay consistent with the development pace of solar thermal tower
power generation techniques, some countries have been developing
software programs since the 1980s, such as UHC, HFLCAL, RCELL,
DELSOL, MIRVAL, FIAT LUX, and SolTrace, and these programs have
been used in the analysis and design of heliostat fields and entire solar