Page 64 - Design of Solar Thermal Power Plants
P. 64
56 2. THE SOLAR RESOURCE AND METEOROLOGICAL PARAMETERS
20
15
10
5
ET/min 0
-5
-10
-15
0 30 60 90 120 150 180 210 240 270 300 330 360
Date serial number
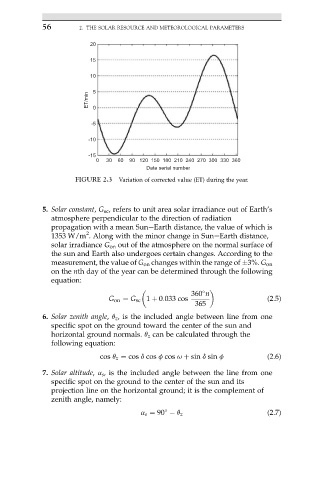
FIGURE 2.3 Variation of corrected value (ET) during the year.
5. Solar constant, G sc , refers to unit area solar irradiance out of Earth’s
atmosphere perpendicular to the direction of radiation
propagation with a mean SuneEarth distance, the value of which is
2
1353 W/m . Along with the minor change in SuneEarth distance,
solar irradiance G on out of the atmosphere on the normal surface of
the sun and Earth also undergoes certain changes. According to the
measurement, the value of G on changes within the range of 3%. G on
on the nth day of the year can be determined through the following
equation:
360 n
G on ¼ G sc 1 þ 0:033 cos (2.5)
365
6. Solar zenith angle, q z , is the included angle between line from one
specific spot on the ground toward the center of the sun and
horizontal ground normals. q z can be calculated through the
following equation:
cos q z ¼ cos d cos f cos u þ sin d sin f (2.6)
7. Solar altitude, a s , is the included angle between the line from one
specific spot on the ground to the center of the sun and its
projection line on the horizontal ground; it is the complement of
zenith angle, namely:
a s ¼ 90 q z (2.7)