Page 221 - Designing Autonomous Mobile Robots : Inside the Mindo f an Intellegent Machine
P. 221
Chapter 13
There are normally two thresholds used by the router in a force field map. The higher of
these thresholds is the level at which the robot is prohibited from using the posi-
tion. A lower threshold may also be specified. For areas with field strength below this
lower threshold, the router is allowed to use the shortest path and not follow the
valley floor.
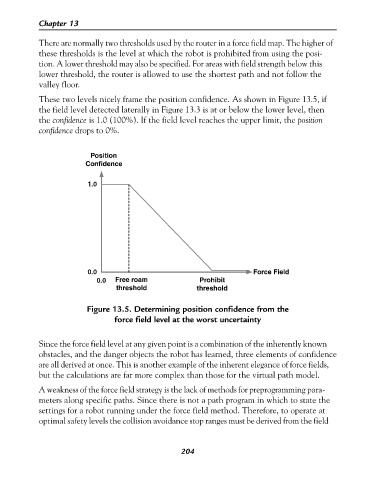
These two levels nicely frame the position confidence. As shown in Figure 13.5, if
the field level detected laterally in Figure 13.3 is at or below the lower level, then
the confidence is 1.0 (100%). If the field level reaches the upper limit, the position
confidence drops to 0%.
Position
Confidence
1.0
0.0 Force Field
0.0 Free roam Prohibit
threshold threshold
Figure 13.5. Determining position confidence from the
force field level at the worst uncertainty
Since the force field level at any given point is a combination of the inherently known
obstacles, and the danger objects the robot has learned, three elements of confidence
are all derived at once. This is another example of the inherent elegance of force fields,
but the calculations are far more complex than those for the virtual path model.
A weakness of the force field strategy is the lack of methods for preprogramming para-
meters along specific paths. Since there is not a path program in which to state the
settings for a robot running under the force field method. Therefore, to operate at
optimal safety levels the collision avoidance stop ranges must be derived from the field
204