Page 218 - Designing Autonomous Mobile Robots : Inside the Mindo f an Intellegent Machine
P. 218
Instilling Pain, Fear and Confidence
Danger = Inherent_danger + Learned_danger
In the case of the virtual path method of navigation, the risk must be implied from
other parameters. One indicator can be the collision avoidance settings. Paths in narrow
areas must use closer stop distances applied to the collision avoidance in order to
execute.
Thus, if the forward stop distance is beyond some relatively high threshold, there is
no inherent danger implied from it. If it is less than this value, then an inherent
danger confidence factor is calculated proportionally. The same is done for the side-
stop ranges, and these two factors are multiplied by each other. Therefore, the robot
knows the inherent danger factor from these settings.
Inherent
path
confidence
1.0
programmed
0.0 stop distance
0.0 0.3 2.0 in meters
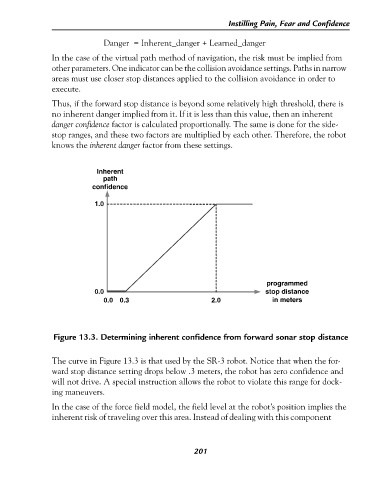
Figure 13.3. Determining inherent confidence from forward sonar stop distance
The curve in Figure 13.3 is that used by the SR-3 robot. Notice that when the for-
ward stop distance setting drops below .3 meters, the robot has zero confidence and
will not drive. A special instruction allows the robot to violate this range for dock-
ing maneuvers.
In the case of the force field model, the field level at the robot’s position implies the
inherent risk of traveling over this area. Instead of dealing with this component
201