Page 232 - Designing Sociable Robots
P. 232
breazeal-79017 book March 18, 2002 14:20
Social Constraints on Animate Vision 213
Ballistic saccade
to new target
Left eye
Vergence
angle
Smooth pursuit
Right eye
and vergence
co-operate to track
object
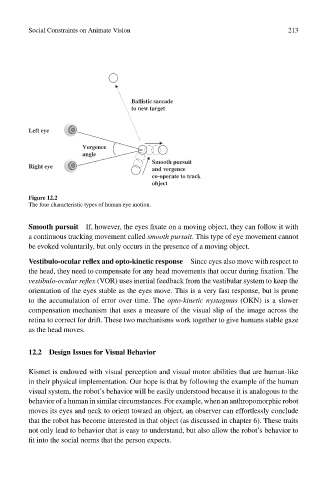
Figure 12.2
The four characteristic types of human eye motion.
Smooth pursuit If, however, the eyes fixate on a moving object, they can follow it with
a continuous tracking movement called smooth pursuit. This type of eye movement cannot
be evoked voluntarily, but only occurs in the presence of a moving object.
Vestibulo-ocular reflex and opto-kinetic response Since eyes also move with respect to
the head, they need to compensate for any head movements that occur during fixation. The
vestibulo-ocular reflex (VOR) uses inertial feedback from the vestibular system to keep the
orientation of the eyes stable as the eyes move. This is a very fast response, but is prone
to the accumulation of error over time. The opto-kinetic nystagmus (OKN) is a slower
compensation mechanism that uses a measure of the visual slip of the image across the
retina to correct for drift. These two mechanisms work together to give humans stable gaze
as the head moves.
12.2 Design Issues for Visual Behavior
Kismet is endowed with visual perception and visual motor abilities that are human-like
in their physical implementation. Our hope is that by following the example of the human
visual system, the robot’s behavior will be easily understood because it is analogous to the
behavior of a human in similar circumstances. For example, when an anthropomorphic robot
moves its eyes and neck to orient toward an object, an observer can effortlessly conclude
that the robot has become interested in that object (as discussed in chapter 6). These traits
not only lead to behavior that is easy to understand, but also allow the robot’s behavior to
fit into the social norms that the person expects.