Page 30 - Digital Analysis of Remotely Sensed Imagery
P. 30
Overview 3
the system. Common input devices include scanners that are able to
convert analog images into a digital format quickly and drives that
allow data stored in the external media to be read into the computer.
Standard output devices include printers and plotters. Printers can
print results, usually small in size, in black and white, or color. A
plotter is able to print a large map of classified results. Other peripheral
devices include a few ports and drives that can read data stored in
special media. Disk drives and special drives for CD read-only
memory (CD-ROM) and memory sticks are so universal to all desktop
and laptop computers that they can hardly be regarded as peripheral
devices any more.
1.2 Features of Digital Image Analysis
Analysis of remotely sensed data in the digital environment differs
drastically from the familiar visual interpretation of satellite images. The
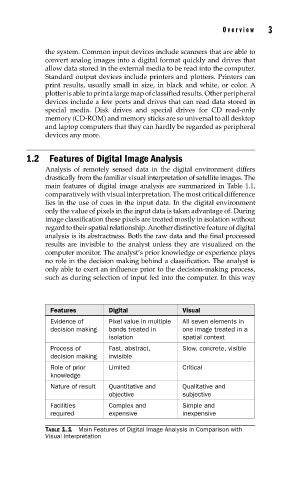
main features of digital image analysis are summarized in Table 1.1,
comparatively with visual interpretation. The most critical difference
lies in the use of cues in the input data. In the digital environment
only the value of pixels in the input data is taken advantage of. During
image classification these pixels are treated mostly in isolation without
regard to their spatial relationship. Another distinctive feature of digital
analysis is its abstractness. Both the raw data and the final processed
results are invisible to the analyst unless they are visualized on the
computer monitor. The analyst’s prior knowledge or experience plays
no role in the decision making behind a classification. The analyst is
only able to exert an influence prior to the decision-making process,
such as during selection of input fed into the computer. In this way
Features Digital Visual
Evidence of Pixel value in multiple All seven elements in
decision making bands treated in one image treated in a
isolation spatial context
Process of Fast, abstract, Slow, concrete, visible
decision making invisible
Role of prior Limited Critical
knowledge
Nature of result Quantitative and Qualitative and
objective subjective
Facilities Complex and Simple and
required expensive inexpensive
TABLE 1.1 Main Features of Digital Image Analysis in Comparison with
Visual Interpretation