Page 185 - Distillation theory
P. 185
P1: JPJ/FFX P2: FCH/FFX QC: FCH/FFX T1: FCH
0521820928c05 CB644-Petlyuk-v1 June 11, 2004 20:15
5.6 Conditions of Section Trajectories Joining and Methods 159
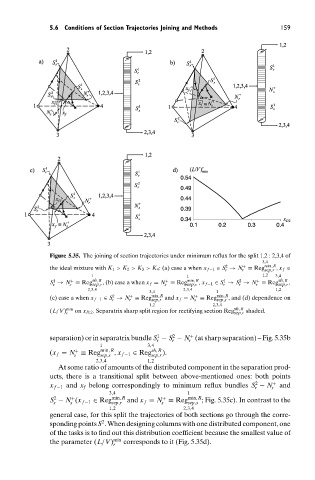
Figure 5.35. The joining of section trajectories under minimum reflux for the split 1,2 : 2,3,4 of
3,4
2
the ideal mixture with K 1 > K 2 > K 3 > K 4 : (a) case a when x f −1 ∈ S → N ≡ Reg min,R , x f ∈
+
r r sep,r
1 1 1,2 3,4
1
2
1
+
+
+
S → N ≡ Reg sh,R , (b) case a when x f = N ≡ Reg min,R , x f −1 ∈ S → S → N ≡ Reg sh,R ,
sep,r
s
sep,s
s
r
s
r
r
sep,r
2,3,4 2,3,4 1,2
3,4 1
2
+
+
(c) case a when x f −1 ∈ S → N ≡ Reg min,R and x f = N ≡ Reg min,R , and (d) dependence on
r
s
sep,s
sep,r
r
1,2 2,3,4
(L/V) min on x D,2 . Separatrix sharp split region for rectifying section Reg sh,R shaded.
r
sep,r
1
2
separation) or in separatrix bundle S − S − N (at sharp separation) – Fig. 5.35b
+
r
r
r
1 3,4
(x f = N ≡ Reg min,R , x f −1 ∈ Reg sh,R ).
+
s
sep,s
sep,r
2,3,4 1,2
At some ratio of amounts of the distributed component in the separation prod-
ucts, there is a transitional split between above-mentioned ones: both points
2
x f −1 and x f belong correspondingly to minimum reflux bundles S − N r + and
r
3,4 1
2
+
+
S − N (x f −1 ∈ Reg min,R and x f = N ≡ Reg min,R ; Fig. 5.35c). In contrast to the
s s sep,r s sep,s
1,2 2,3,4
general case, for this split the trajectories of both sections go through the corre-
2
sponding points S . When designing columns with one distributed component, one
of the tasks is to find out this distribution coefficient because the smallest value of
the parameter (L/V) min corresponds to it (Fig. 5.35d).
r