Page 327 - Distillation theory
P. 327
P1: JPJ/FFX P2: FCH/FFX QC: FCH/FFX T1: FCH
0521820928c08 CB644-Petlyuk-v1 June 11, 2004 20:20
8.5 Multicomponent Azeotropic Mixtures: Automatic Sequencing and Selection 301
3 3 E 3
a) b) c) 35
E 24135
24153
42513 24153 E
D D
45213 42513
1 4 2 D 24 4 2 5
4 4 D
d) e)
D
24
42153
42153
E
42135
2 5 3 E 24 5
j
t(3)
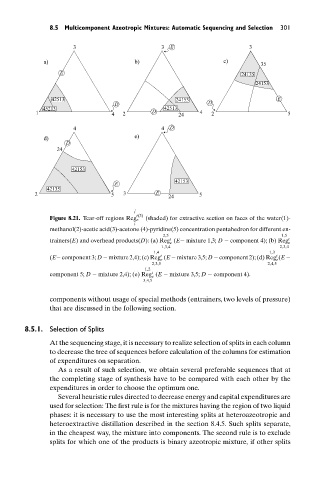
Figure 8.21. Tear-off regions Reg e (shaded) for extractive section on faces of the water(1)-
i
methanol(2)-acetic acid(3)-acetone (4)-pyridine(5) concentration pentahedron for different en-
2,5 1,5
t
trainers(E) and overhead products(D): (a) Reg (E− mixture 1,3; D − component 4); (b) Reg t e
e
1,3,4 2,3,4
1,4 1,3
t t
(E− component 3; D − mixture 2,4); (c) Reg (E − mixture 3,5; D − component 2); (d) Reg (E −
e
e
2,3,5 2,4,5
1,2
t
component 5; D − mixture 2,4); (e) Reg (E − mixture 3,5; D − component 4).
e
3,4,5
components without usage of special methods (entrainers, two levels of pressure)
that are discussed in the following section.
8.5.1. Selection of Splits
At the sequencing stage, it is necessary to realize selection of splits in each column
to decrease the tree of sequences before calculation of the columns for estimation
of expenditures on separation.
As a result of such selection, we obtain several preferable sequences that at
the completing stage of synthesis have to be compared with each other by the
expenditures in order to choose the optimum one.
Several heuristic rules directed to decrease energy and capital expenditures are
used for selection: The first rule is for the mixtures having the region of two liquid
phases: it is necessary to use the most interesting splits at heteroazeotropic and
heteroextractive distillation described in the section 8.4.5. Such splits separate,
in the cheapest way, the mixture into components. The second rule is to exclude
splits for which one of the products is binary azeotropic mixture, if other splits