Page 331 - Dust Explosions in the Process Industries
P. 331
300 Dust Explosions in the Process Industries
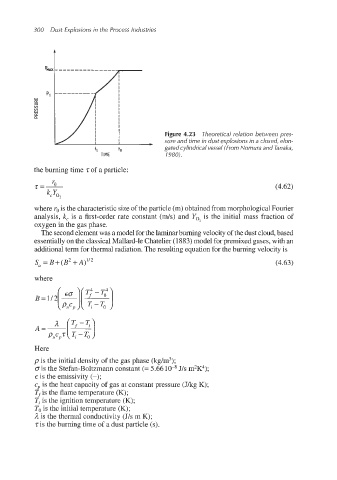
Figure 4.23 Theoretical relation between pres-
sure and time in dust explosions in a closed, elon-
gated cylindrical vessel (From Nomura and Tanaka,
+I +O
TIME 19801.
the burning time zof a particle:
T=- TO (4.62)
kcyo,
where rois the characteristic size of the particle (m) obtained from morphologicalFourier
analysis, k, is a first-order rate constant (ds) and Yo, is the initial mass fraction of
oxygen in the gas phase.
The second elementwas a model for the laminarburning velocity of the dust cloud,based
essentiallyon the classical Mallard-le Chatelier (1883) model for premixed gases, with an
additionalterm for thermal radiation. The resulting equation for the burning velocity is
S, = B+(B' +A)"' (4.63)
where
Here
p is the initial density of the gas phase (kg/m3);
cr is the Stefan-Boltzmann constant (= 5.66 lo-*J/s m2K4);
E is the emissivity (-);
cpis the heat capacity of gas at constant pressure (Jkg K);
Tf is the flame temperature (K);
is the ignition temperature (K);
Tois the initial temperature (K);
2, is the thermal conductivity (J/s m K);
zis the burning time of a dust particle (s).