Page 574 - Dust Explosions in the Process Industries
P. 574
Assessment of lgnitability 54 7
7.1 9.2
LAB0RAT0RY TESTS
In the United States,as described by Dorsett et al. (1960),two standard test methods were
traditionally used. In both tests, the dust was dispersed in the appropriate gas mixture,
from above, into a fairly narrow vertical tube of internal diameter 38 mm and exposed
to anignition source.The apparatusis similarto the Godbert-Greenwaldfurnace described
in Section 7.8. In the first test, the ignition source was an electric spark; in the second
test, the hot tubie wall. Usually, the limiting gas compositions for flame propagation
obtained for the same dust from the two tests differed significantly, the hot surface test
yielding lower critical permissible oxygen contents than the spark test.
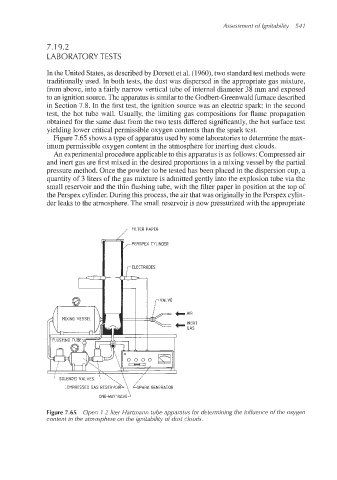
Figure 7.65 shows a type of apparatus used by some laboratories to determine the max-
imum permissible oxygen content in the atmospherefor inerting dust clouds.
An experimentalprocedure applicableto this apparatus is as follows: Compressed air
and inert gas are first mixed in the desired proportions in a mixing vessel by the partial
pressure method. Once the powder to be tested has been placed in the dispersion cup, a
quantity of 3 liters of the gas mixture is admitted gently into the explosion tube via the
small reservoir and the thin flushing tube, with the filter paper in position at the top of
the Berspex cylinder. During this process,the air that was originally in the Perspex cylin-
der leaks to the atmosphere. The small reservoir is now pressurized with the appropriate
,,-FILTER PAPER
PERSPEX CYLINOER
AIR
MIXING VESSEL
INERT
GAS
COMPRESSED GAS RESE ARK GENERATOR
Figure 7.65 Open 1.2 liter Hartmann tube apparatus for determining the influence of the oxygen
content in the atmosphere on the ignitability of dust clouds.