Page 109 - Dynamics and Control of Nuclear Reactors
P. 109
8.10 Important reactivity feedbacks and control strategies 103
Full-length part-strength control rods have lower poison concentrations through-
out the rods than full strength rods. Like full-length full-strength control rods, they
affect local power density, but not as strongly.
Part-length control rods have neutron absorber only near the tip. They can reduce
local power density at in-core regions without strongly affecting the power density in
regions behind the absorber region. They are useful in controlling the power distribution.
Heavy water reactors (CANDU) use in-core chambers where light water can be
introduced. Increasing light water in the chambers decreases reactivity and reduces
the local power production.
Fixed-position burnable poison rods are installed in high power density regions
before the reactor goes into operation. They affect the local power density and their
strength decreases as the reactor operates and the poison is transmuted by neutron
absorption. These are common in BWRs. BWR fuel assemblies also contain “water
rods” that help increase moderation and thus reactivity.
8.10 Important reactivity feedbacks and control strategies
for various reactor types
Chapters 12–14 address various reactor types and their important reactivity
feedbacks and control strategies.
Exercises
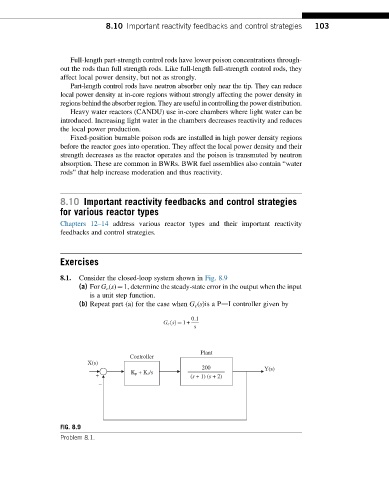
8.1. Consider the closed-loop system shown in Fig. 8.9
(a) For G c (s)¼1, determine the steady-state error in the output when the input
is a unit step function.
(b) Repeat part (a) for the case when G c (s)is a PdI controller given by
0:1
G c sðÞ ¼ 1+
s
Plant
Controller
X(s)
200 Y(s)
K p + Ki/s
+ (s + 1) (s + 2)
_
FIG. 8.9
Problem 8.1.