Page 250 - Dynamics and Control of Nuclear Reactors
P. 250
APPENDIX B Advanced reactors 251
B.7 Small reactors
B.7.1 Introduction
Small reactors are those with power levels of 300 MWe or less. All of the reactors
discussed in Section B.3 also have small reactor versions. Since the designs are gen-
erally smaller, but with similar components as large reactor designs, design features
are not provided here. The design of small modular reactors is integral in nature, with
reactor core, heat exchangers/steam generators, coolant pumps, and control rod drive
mechanisms contained in a large vessel. A summary description of instrumentation
and control systems in small reactors is given in Ref. [28].
B.7.2 Incentives
The incentive for small reactors is faster construction and lower incremental cost to
the purchaser, thereby adding capacity as needed and adding debt incrementally. The
smaller components allow even greater shop fabrication than large advanced reac-
tors. The smaller components also permit placing more components inside the pri-
mary containment, thereby enhancing safety. Small reactors can be placed in a
single-reactor facility in regions where power demand is low or in multi-reactor sites
where reactors are added as demand increases.
B.7.3 Small reactor list
Many small reactor designs are under development (too many for descriptions here).
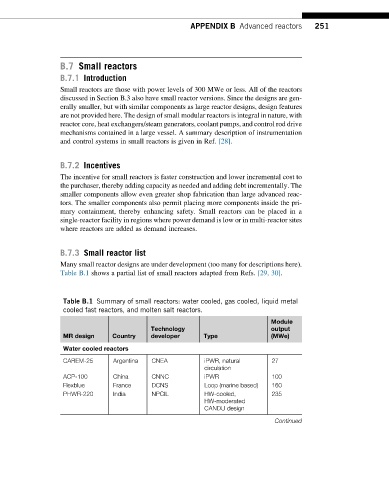
Table B.1 shows a partial list of small reactors adapted from Refs. [29, 30].
Table B.1 Summary of small reactors: water cooled, gas cooled, liquid metal
cooled fast reactors, and molten salt reactors.
Module
Technology output
MR design Country developer Type (MWe)
Water cooled reactors
CAREM-25 Argentina CNEA iPWR, natural 27
circulation
ACP-100 China CNNC iPWR 100
Flexblue France DCNS Loop (marine based) 160
PHWR-220 India NPCIL HW-cooled, 235
HW-moderated
CANDU design
Continued