Page 261 - Dynamics and Control of Nuclear Reactors
P. 261
262 APPENDIX C Basic reactor physics
Incident neutron data / ENDF/B-VII.1 / U238 / MT = 102: (z, Y ) / Cross section
10000
1000
100
Cross-section (b) 0,1 1 Incident energy (meV)
10
g
1/v region
e
g
g
gi
vr
/
/
on
/
/
1/ 1/v region
V)
d
nt
nt
nt
ene
ene
ene
rg
rg
n
n
n
y
(m
y
rg
y
eV)
m
n
V)
n
n
n
n
n
m
ide
ide
ide
Inc
c
c
d
d
d
d
d
d
d
0,01
n
rg
(
n
Inc
Inc ide nt ene rg y y y ( (m eV) ) )
Incident energy (meV)
rg
Incident energyy (meV)
0,001
1E-4
1E-11 1E-10 1E-9 1E-8 1E-7 1E-6 1E-5 1E-4 0,001 0,01 0,1 1 10
Incident energy (MeV)
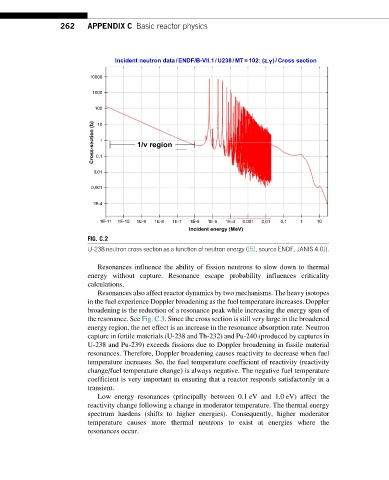
FIG. C.2
U-238 neutron cross section as a function of neutron energy ([5], source ENDF, JANIS 4.0]).
Resonances influence the ability of fission neutrons to slow down to thermal
energy without capture. Resonance escape probability influences criticality
calculations.
Resonances also affect reactor dynamics by two mechanisms. The heavy isotopes
in the fuel experience Doppler broadening as the fuel temperature increases. Doppler
broadening is the reduction of a resonance peak while increasing the energy span of
the resonance. See Fig. C.3. Since the cross section is still very large in the broadened
energy region, the net effect is an increase in the resonance absorption rate. Neutron
capture in fertile materials (U-238 and Th-232) and Pu-240 (produced by captures in
U-238 and Pu-239) exceeds fissions due to Doppler broadening in fissile material
resonances. Therefore, Doppler broadening causes reactivity to decrease when fuel
temperature increases. So, the fuel temperature coefficient of reactivity (reactivity
change/fuel temperature change) is always negative. The negative fuel temperature
coefficient is very important in ensuring that a reactor responds satisfactorily in a
transient.
Low energy resonances (principally between 0.1 eV and 1.0 eV) affect the
reactivity change following a change in moderator temperature. The thermal energy
spectrum hardens (shifts to higher energies). Consequently, higher moderator
temperature causes more thermal neutrons to exist at energies where the
resonances occur.