Page 201 - E-Bussiness and E-Commerce Management Strategy, Implementation, and Practice
P. 201
M03_CHAF9601_04_SE_C03.QXD:D01_CHAF7409_04_SE_C01.QXD 16/4/09 11:09 Page 168
168 Part 1 Introduction
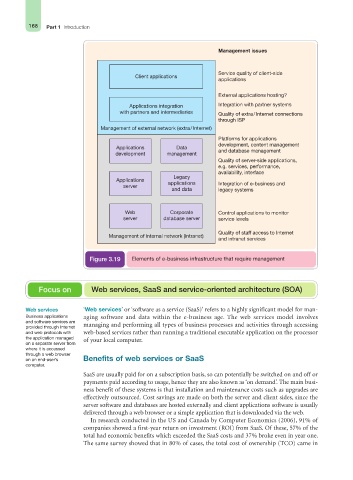
Management issues
Service quality of client-side
Client applications
applications
External applications hosting?
Applications integration Integration with partner systems
with partners and intermediaries Quality of extra/Internet connections
through ISP
Management of external network (extra /Internet)
Platforms for applications
development, content management
Applications Data
development management and database management
Quality of server-side applications,
e.g. services, performance,
availability, interface
Legacy
Applications
applications Integration of e-business and
server
and data legacy systems
Web Corporate Control applications to monitor
server database server service levels
Quality of staff access to Internet
Management of internal network (intranet)
and intranet services
Figure 3.19 Elements of e-business infrastructure that require management
Focus on Web services, SaaS and service-oriented architecture (SOA)
Web services ‘Web services’ or ‘software as a service (SaaS)’ refers to a highly significant model for man-
Business applications aging software and data within the e-business age. The web services model involves
and software services are
provided through Internet managing and performing all types of business processes and activities through accessing
and web protocols with web-based services rather than running a traditional executable application on the processor
the application managed of your local computer.
on a separate server from
where it is accessed
through a web browser
on an end-user’s Benefits of web services or SaaS
computer.
SaaS are usually paid for on a subscription basis, so can potentially be switched on and off or
payments paid according to usage, hence they are also known as ‘on demand’. The main busi-
ness benefit of these systems is that installation and maintenance costs such as upgrades are
effectively outsourced. Cost savings are made on both the server and client sides, since the
server software and databases are hosted externally and client applications software is usually
delivered through a web browser or a simple application that is downloaded via the web.
In research conducted in the US and Canada by Computer Economics (2006), 91% of
companies showed a first-year return on investment (ROI) from SaaS. Of these, 57% of the
total had economic benefits which exceeded the SaaS costs and 37% broke even in year one.
The same survey showed that in 80% of cases, the total cost of ownership (TCO) came in