Page 203 - E-Bussiness and E-Commerce Management Strategy, Implementation, and Practice
P. 203
M03_CHAF9601_04_SE_C03.QXD:D01_CHAF7409_04_SE_C01.QXD 16/4/09 11:09 Page 170
170 Part 1 Introduction
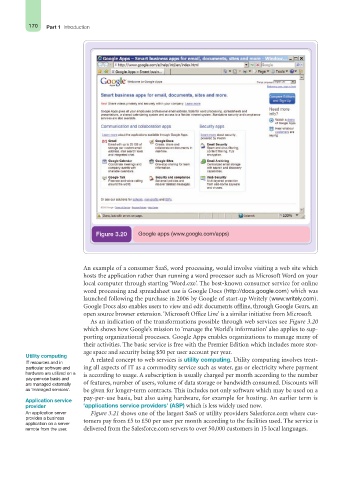
Figure 3.20 Google apps (www.google.com/apps)
An example of a consumer SaaS, word processing, would involve visiting a web site which
hosts the application rather than running a word processor such as Microsoft Word on your
local computer through starting ‘Word.exe’. The best-known consumer service for online
word processing and spreadsheet use is Google Docs (http://docs.google.com) which was
launched following the purchase in 2006 by Google of start-up Writely (www.writely.com).
Google Docs also enables users to view and edit documents offline, through Google Gears, an
open source browser extension.‘Microsoft Office Live’ is a similar initiative from Microsoft.
As an indication of the transformations possible through web services see Figure 3.20
which shows how Google’s mission to ‘manage the World’s information’ also applies to sup-
porting organizational processes. Google Apps enables organizations to manage many of
their activities. The basic service is free with the Premier Edition which includes more stor-
age space and security being $50 per user account per year.
Utility computing
A related concept to web services is utility computing. Utility computing involves treat-
IT resources and in
particular software and ing all aspects of IT as a commodity service such as water, gas or electricity where payment
hardware are utilized on a is according to usage. A subscription is usually charged per month according to the number
pay-per-use basis and
are managed externally of features, number of users, volume of data storage or bandwidth consumed. Discounts will
as ‘managed services’. be given for longer-term contracts. This includes not only software which may be used on a
pay-per-use basis, but also using hardware, for example for hosting. An earlier term is
Application service
provider ‘applications service providers’ (ASP) which is less widely used now.
An application server Figure 3.21 shows one of the largest SaaS or utility providers Salesforce.com where cus-
provides a business
application on a server tomers pay from £5 to £50 per user per month according to the facilities used. The service is
remote from the user. delivered from the Salesforce.com servers to over 50,000 customers in 15 local languages.