Page 354 - E-Bussiness and E-Commerce Management Strategy, Implementation, and Practice
P. 354
M05_CHAF9601_04_SE_C05.QXD:D01_CHAF7409_04_SE_C01.QXD 16/4/09 11:12 Page 321
Chapter 5 E-business strategy 321
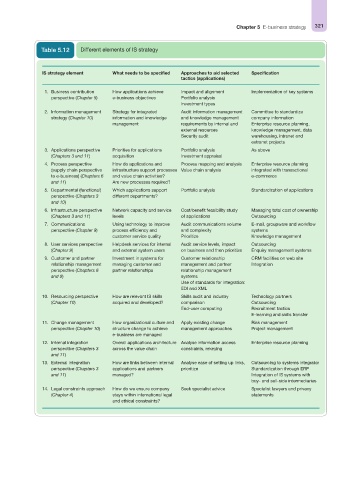
Table 5.12 Different elements of IS strategy
IS strategy element What needs to be specified Approaches to aid selected Specification
tactics (applications)
1. Business contribution How applications achieve Impact and alignment Implementation of key systems
perspective (Chapter 5) e-business objectives Portfolio analysis
Investment types
2. Information management Strategy for integrated Audit information management Committee to standardize
strategy (Chapter 10) information and knowledge and knowledge management company information
management requirements by internal and Enterprise resource planning,
external resources knowledge management, data
Security audit warehousing, intranet and
extranet projects
3. Applications perspective Priorities for applications Portfolio analysis As above
(Chapters 3 and 11) acquisition Investment appraisal
4. Process perspective How do applications and Process mapping and analysis Enterprise resource planning
(supply chain perspective infrastructure support processes Value chain analysis integrated with transactional
to e-business) (Chapters 6 and value chain activities? e-commerce
and 11) Are new processes required?
5. Departmental (functional) Which applications support Portfolio analysis Standardization of applications
perspective (Chapters 3 different departments?
and 10)
6. Infrastructure perspective Network capacity and service Cost/benefit feasibility study Managing total cost of ownership
(Chapters 3 and 11) levels of applications Outsourcing
7. Communications Using technology to improve Audit communications volume E-mail, groupware and workflow
perspective (Chapter 9) process efficiency and and complexity systems
customer service quality Prioritize Knowledge management
8. User services perspective Helpdesk services for internal Audit service levels, impact Outsourcing
(Chapter 9) and external system users on business and then prioritize Enquiry management systems
9. Customer and partner Investment in systems for Customer relationship CRM facilities on web site
relationship management managing customer and management and partner Integration
perspective (Chapters 6 partner relationships relationship management
and 9) systems
Use of standards for integration:
EDI and XML
10. Resourcing perspective How are relevant IS skills Skills audit and industry Technology partners
(Chapter 10) acquired and developed? comparison Outsourcing
End-user computing Recruitment tactics
E-learning and skills transfer
11. Change management How organizational culture and Apply existing change Risk management
perspective (Chapter 10) structure change to achieve management approaches Project management
e-business are managed
12. Internal integration Overall applications architecture Analyse information access Enterprise resource planning
perspective (Chapters 3 across the value chain constraints, rekeying
and 11)
13. External integration How are links between internal Analyse ease of setting up links, Outsourcing to systems integrator
perspective (Chapters 3 applications and partners prioritize Standardization through ERP
and 11) managed? Integration of IS systems with
buy- and sell-side intermediaries
14. Legal constraints approach How do we ensure company Seek specialist advice Specialist lawyers and privacy
(Chapter 4) stays within international legal statements
and ethical constraints?